ECO 212 - Macroeconomics
Exam 2 REVIEW - 19th edition
Be sure to also see the "EXAM REVIEW" link on our Blackboard
site.
We have not thoroughly completed all the chapters in class that
will be covered on the unit 2 exam. It is suggested that you read all
of the chapters (be sure to see the exact pages to read on our
"ASSIGNMENTS" page) and concentrate on the following sections:
Chapter 12 - Thoroughly covered in
class
Chapter 9 - Thoroughly covered in class
So here we'll just discuss Ch. 7, Ch.
8, and Ch. 22W
Chapter 7 - Measuring Domestic Output (RDO),
National Income, and the Price Level
Study Guide, especially pp. 80-82: #2, 4, 6, 7, 9-13, 15, 16-19,
23-30
GDP (pp. 130-132)
- know the definition of GDP
- "the total MARKET VALUE
- of all FINAL goods and services
- PRODUCED in an economy in one year."
- know why we use the "market value", or the monetary value
($$$) to measure RDO
- know why they include only "final goods and services"
- avoiding double counting / what is double counting?
- what are final goods?
- what are intermediate goods? why are they NOT added to
GDP?
- GDP measures PRODUCTION therefore "GDP Excludes Nonproductive
Transactions"
Expenditures Approach (p.
132-135)
- Be able to calculate GDP from a table of data like that on pp.
147-148 (question #4a) using
the expenditures approach
- GDP = C + I + G + Xn
- HINT: this is important
Income Approach (pp.
136-138)
- Understand how summing up the income earned by the
factors of production (resources) can give us a measure of GDP
which is production. (See p. 132 "Two Ways of Looking at GDP:
Spending and Income.)
- Know the difference between gross investment and net
investment
Other National Accounts (pp.
138-139)
- Understand and be able to calculate NDP (question
#4a pp. 147-148)
- Know and be able to calculate NI (national income)
NI = wages + rent + interest + profits
(profits = corp. profits + proprietor's income)
- Know definition of NI (income EARNED by the resources)
- Know definition of PI (income RECEIVED)
- Know definition of DI (SPENDABLE income)
Nominal and Real GDP (pp.
141-143)
- You must be able to convert nominal GDP to real GDP and know
the differences between these concepts
[Be able to fill in the blanks on Table 7.5, page 141, and
study guide p. 82, multiple-choice questions # 23-27]
- nominal GDP = SUM (P current year x Q current year)
- real GDP = SUM (P base year x Q current year)
- Why use real GDP?
- To measure RDO. It is possible for nominal GDP to increase
even though RDO decreased. How?
- nominal GDP
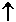 a
little = SUM (P
a
little = SUM (P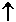 alot
x Q
alot
x Q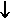 a little)
a little)
- Q is RDO
- real GDP = nominal GDP / price index
Shortcomings of GDP (pp.
143-144)
- This is important
- Know whether each of these cause GDP to OVERSTATE or
UNDERSTATE Economic Well-Being
- non-market transactions are not counted (GDP
understates)
- leisure is not add as a positive (GDP
understates)
- improved product quality but same price (GDP
understates)
- the composition and distribution of output
(e.g.. produce many guns and drugs: GDP
but ¯Well-Being (GDP
overstates)
- per capita output (GDP understates well-being in
countries with small populations and overstates in countries
with large populations)
- GDP and the environment (GDP overstates)
- the underground economy not included (GDP
understates)
- resource depletion not accounted for (GDP
overstates)
- noneconomic sources of well-being (GDP
understates)
- We will also cover some of this in the lecture on Measures of
Development (LDCs)
Chapter 8 - Economic Growth
Study Guide, especially multiple-choice questions: pp. 92-94, #1
2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 13, 15,17, 18, 20, 25
Economic Growth (pp.
149-151)
- "Two Definitions" - We'll use 2 DIFFERENT definitions:
- Ch. 1 definition (see pp. 15-16) - an increase in the
ABILITY to produce a larger total output.
- This is "Economic Growth" on our 5Es chart.
- On our graphs this is shifting the PPC outwards and an
increase in AS.
- Ch. 8 definition - an increase in output (real GDP).
- This is "Full Employment" and "Productive Efficiency" on
our 5Es chart.
- On our graphs this is going from a point within the PPC
to a point closer to the PPC or an increase in AD
- Our textbook's two definitions on pp. 149 are different:
- "an increase in real GDP occurring over some time
period" includes BOTH of the two definitions we use in class
(see above).
- "an increase in real GDP per capita occurring
over some time period" is an increase in real GDP PER
PERSON. GDP per capita is GDP divided by the
population.
Modern Economic Growth
(pp.152-155)
Institutional Structures That
Promote Growth (pp. 155-156)
Determinants of Growth (pp.
152-153)
- "Supply Factors" help to increase the ABILITY to produces
goods and services.
- This shifts the AS curve to the right
- and SHIFTS the production possibilities curve outwards (Ch.
1 definition).
- "Demand Factors" and the "Efficiency Factor" help ACHIEVE the
potential level of output.
- This shifts the AD to the right
- and does not shift the production possibilities curve (Ch.
8 definition).
Production Possibilities Analysis
(pp. 157-158)
- Know the difference between:
- production,
- productive efficiency,
- and productivity
Accounting for Growth (pp.
158-162)
The Rise in the Averaqge Rate of
Productivity Growth (162-165)
Is Growth Desirable and
Sustainable? (165-167)
Chapter 22W - Growth and the LDCs
I use the term "Less Developed Countries" or "LDCs" for the
world's poor countries and "More Developed Countries" or "MDCs" for
the world's richer countries. The authors of our textbook use the
term "developing countries" or "DVCs" for the poor countries and
"Industrially Advanced Countries" or "IACs" for the richer
countries.
Study Guide, pp. 256-257: especially questions: #1, 2, 4-8, 12, 16,
19
The Rich and the Poor pp. 2-4
(Measures of Economic Development)
Obstacles to Economic
Development (pp. 4-11)
- How does "use their existing supplies of resources more
efficiently" and " expand their available supplies of resources"
fit into our 5Es concept?
- Pay close attention to the role of population growth. How does
population growth affect the growth in GDP PER CAPITA?
- "Low Labor Productivity" and "Capital Accumulation" provides
good examples to reinforce concepts also covered in chapter 9
(Economic Growth)
The Vicious Circle (pp.
11-12)
- more on population growth
Role of Government (pp.
12-13)
Role of Advanced Nations (pp.
14-18)
- Think about what might help the LDCs (DVCs) the most: TRADE or
AID?
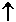 a
little = SUM (P
a
little = SUM (P alot
x Q
alot
x Q a little)
a little)