
|
|
|
|
Realms (Figure I-1, pp. 4-5 with modifications)
Developing
Middle America
South America
North Africa and Southwest Asia
Sub-Saharan Africa
China
South Asia
Southeast Asia
The Pacific RealmDeveloped
Europe
North America
Russia
Japan
Australia - New Zealand
Continents
North America
South America
Europe
Asia
Africa
Australia
Antarctica
Water Bodies
Atlantic Ocean
Pacific Ocean
Indian Ocean
Mediterranean Sea
Countries/States
United States
Russia
China
Japan
India
Illinois
Mountains
Rocky Mountains
Alps
Himalayas
Andes
Climatic Regions (Figure I-7, pp. 16-17 and Figure I-8, p. 18)
Tropical Rain Forests (A Climates)
Deserts (BW climates)
Major Population Clusters (Figure I-9, pp. 22-23)
East Asia
South Asia
Europe
de Blij: pp. 2-7, 25-27, 33-39, 52 (box), A8-A14 (appendix C)
realm
region
regional criteria
spatial perspective
history analogy
boundary model (p.52 box)
core
periphery
I-1 World Geographic Realms (as modified in class)
I-12 World Realms and their Regions
1. Understand the geographic point of view and its uses. What is geography? What kinds of issues are included in the study of geography? Why?
2. Understand the importance of the regional concept in the study of geography and be able to delineate regions by applying the regional criteria..
3. Apply the regional criteria to an area of the developing world. Why is it a realm or region? Why is it divided from adjacent areas?
1. What is a Region?
2. Why do geographers use regions?
3. What criteria could be used to designate a region?
DEFINITION: scientific devices that allow us to make spatial generalizations based on artificial criteria that we establish for the purpose of constructing regions
CRITERIA:
physical
economic
historical
cultural (religion, language, political, other)
population clusters
combinations of criteria
PROPERTIES:
area
location
boundaries are transition zones
boundaries change
QUESTIONS:
1. Where is the realm or region?
2. What criteria is being used to designate this region?
3. How is the realm significantly different from adjacent realm?
(i.e. explain the boundary or transition zones between realms.)
4. What are the significant properties?
ASSIGNMENT: Theme Activity -- See "Assignments" in the Syllabus.
de Blij: pp. 7-20, 23-25, A6-A7 (appendix B)
A climates
B climates
C climates
D climates
Highland climates (H)
plateau
plains
continental drift
physiography
I-4 World Landscapes
I-6 World Precipitation
I-7 World Climates
I-8 World Vegetation
I-9 World Population Distribution
1. Develop an understanding of the spatial distributions of the world's landscapes, precipitation, climates, and vegetation. Be able to use maps to see relationships among these and world events.
2. Locate the world's major population clusters.
3. Understand where people live and why they live there?
4. Human-Environment interaction is an important concept in geography. Students should see connections between human activities and the physical environment.
1. Understand the basic physical geography of the world's
developing realms and their unique physical attributes.
2. Where do people live and why?
1. Apply criteria to realms.
2. Apply criteria to regions within realms.
de Blij: pp. 28-33, 157, 236, 415, appendix A
GDP (GNP)
GDP per capita
LDCs
MDCs
third world
second world
first world
doubling time
rule of 70
primary activities
secondary activities
tertiary activities
quaternary activities
urbanization
infrastructure
literacy
life expectancy
infant mortality
overconsumption
I-11 World Economies
5-2 World Agriculture
World Life Expectancy at Birth
World Population Growth
1. GDP per capita
2. Population Growth
3. Occupational Structure of the Labor Force
4. Urbanization
5. Consumption per capita
6. Infrastructure
7. Social Conditionsliteracy rate
caloric intake
life expectancy
infant mortality
health care
other
1. Understand how each Measure indicates the level of economic development. (What is high? low?)
2. Learn and be able to appropriately use the vocabulary.
3. Apply the measures to the world's realms classifying them into "more developed" and "less developed" categories
4. Begin to appreciate the uses for geographic software programs like PC Globe Maps 'N Facts.
de Blij: pp. 51-55, 338, 235-239
Mexico (IMF video)
South Korea and Tanzania (International Economics)
agrarian revolution
industrial revolution
functional specialization
regional complementarity
capitalism/market economy
central planning
monopoly
regional economic integration
GATT/WTO
trade barriers / protectionism
structural adjustment
IMF
World Bank
exchange rate
privatization
subsidies
price controls
productivity
economic incentives
5 Es
command economy
1. A Move Toward Capitalism (changing economic systems)
2. Freer Trade
3. Economic Development
1. Compare market and command economies.
2. List the arguments of those who support and oppose freer
trade.
3. Understand the arguments of economists in support of free
trade.
4. Explain the goal of the following economic changes often proposed
by the IMF:
a. privatization
b. exchange rate reform
c. removal of price controls
d. debt reduction
e. import liberalization
5. List some examples of regional economic integration.
1. Interpret and compare the Measures of Economic Development for
the world's developing realms.
2. How do people make a living and why?
3. Understand recent economic developments and their resource
base.
|
CHARACTERISTIC |
COMMAND ECONOMY |
MARKET ECONOMY |
|
ownership of resources: |
government ownership |
private ownership |
|
decision making: |
centrally planned |
by the market |
|
motivation: |
"social good" |
self interest and profit |
|
prices and wages: |
set by the government |
set by the market |
|
result: |
inefficiency |
economic efficiency |
|
problems: |
corruption=self interest |
monopoly= inefficiency |
|
OVERALL: |
LESS FOR MORE |
MORE FOR LESS |
The 5 "E"s of Economics |
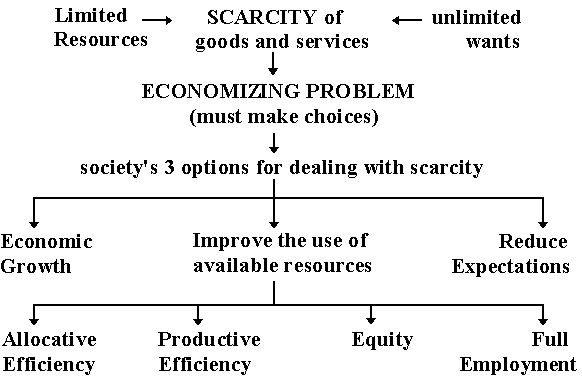
Measures of Economic Development and Maps in the Goode's Atlas |
de Blij: pp. 20-23, 25-27, 56 (box), 56-57, 60-63, 93 (box), 278 (box),
477 (box)
culture
cultural landscape
sequent occupance
nation
state
nation-state
cold war
irredentism
balkanization
devolution
acculturation
transculturation
centripetal and centrifugal forces
coup d'etat
6-1 Religions of the World
1. Be able to define the vocabulary above and give examples from the developing world.
2. How does the cultural diversity found in the developing countries affect their economic and political development? Give examples.
3. Understand the concept of a nation state. Discuss how this is a source of cultural conflicts and political instability.
4. Define and understand the terms balkanization, devolution, and irredentism. Name some countries in where these concepts apply and EXPLAIN.
5. List the centripetal and the centrifugal forces causing unity, or balkanization and devolution, in some countries in the developing world.
Cultural Geography
1. Understand the spatial distribution of religion, language, governments, and other cultural features.
2. Recognize the significance of these distributions.
Diversity and Conflicts
1. Locate cultural and political conflicts.
2. Who is fighting whom?
3. Why?
de Blij p.203-207, 235-240, 276-280, 282, 337-343, 376-382, 423-428, 482-488
colonialism
imperialism
geometric borders
historical geog.
spatial process
spatial diffusion
sequent occupance
culture hearth
Ottoman empire
Mesoamerica
4-4 Caribbean Region: Colonial Spheres ca. 1850
7-6 Sub-Saharan Africa: Colonization and Liberation
10-4 Colonial Spheres in Southeast Asia
(developed by Harper students, Spring, 1994)
1. Economic development modified for benefit of Europe.
2. Inappropriate technologies introduced.
3. Coastal states rose in power while the interior's influence
declined.
4. Political stability declined(?) as national liberation movements
arose.
5. Geometric borders ignored cultural geography.
6. Migration routes closed off.
7. Colonial cities arose.
8. European model of government introduced often contrary to the
traditional culture of direct access and communication.
9. Crude Death Rates decreased resulting in an increase in the rate
of population growth.
10. Colonial transportation networks established connecting the
interior to the coast with few internal connections.
11. Trade patterns directed toward Europe diminishing local regional
complementarities.
12. Dual economies established: a modern European sector along side a
traditional subsistence sector.
13. Introduction of Europeans systems of education.
14. Introduction of European religions
1. Develop a general idea of the major imperial powers in the last two centuries and the locations of their colonies.
2. Understand the effects of colonization.
3. Locate and discuss the world's major ancient culture hearths..
1. Understand precolonial history and its effects today.
2. Understand colonial history (if any) and its effects today.
1. Understand the basic physical geography of the world's developing realms and their unique physical attributes.
2. Where do people live and why?
1. Apply criteria to realms.
2. Apply criteria to regions within realms.
1. Interpret and compare the Measures of Economic Development for
the world's developing realms.
2. How do people make a living and why?
3. Understand recent economic developments and their resource
base.
1. Understand the spatial distribution of religion, language, governments, and other cultural features.
2. Recognize the significance of these distributions.
1. Locate cultural and political conflicts.
2. Who is fighting whom?
3. Why?
1. Understand precolonial history and its effects today.
2. Understand colonial history (if any) and its effects today.
What you can DO versus what do you KNOW.
The point of these objectives is not to memorize but to apply, analyze, and predict. See the "Critical Thinking" section of the syllabus.
de Blij: Chapter 7, Also use index
Sub-Saharan Africa (chapter 7):
|
R&P GEOG |
CULT GEOG |
ECON GEOG |
HIST GEOG |
|
327-333 |
343-346 |
333-337 |
337-343 |
1. Where do people live in Sub-Saharan Africa and why? (R&P GEOG)
2. Locate the major features of Sub-Saharan Africa on a map, including the countries, prominent physical regions, climatic regions, primary rivers, and major water bodies.
3. Explain the rationale for dividing Africa into North Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa and for dividing Sub-Saharan Africa into its regions. (R&P GEOG)
4. Discuss the cultural diversity found in Sub-Saharan Africa and problems associated with it. Compare the concept of a nation-state to the independent states of Sub-Saharan Africa. Discuss how this is a source of cultural conflicts in the region. (CULT GEOG)
5. Describe the unique physical geography of the African continent and the processes responsible for these unique features. (R&P GEOG)
6. Discuss the impact of colonization in Sub-Saharan Africa. Include economic development, political stability, and geometric borders in your discussion. Compare the different styles and policies of colonization used by the Europeans. (HIST GEOG)
7. Identify the major economic activities that occur in Sub-Saharan Africa and understand some of the current economic problems and changes. (ECON GEOG)
8. Define and understand the terms balkanization, devolution, and irredentism. Name some countries in Sub-Saharan Africa where these concepts apply and EXPLAIN. List the centripetal and the centrifugal forces causing balkanization or devolution in those countries. (Examples: Ethiopia and Eritrea, Somalia, Sudan, Rwanda and Burundi, Angola, Mozambique, Liberia, others.) (CULT GEOG)
9. Develop a basic understanding of the development of the current political situation in South Africa.(CULT GEOG)
de Blij --Sub-Saharan Africa (Chapter 7)
rift valley
continental drift
green revolution
sequent occupance
Berlin conference
great escarpment
periodic market
Sahel
nomadism
buffer zone
neocolonialism
Afrikaners
apartheid
homelands
African National Congress (ANC)
Listed below are some suggested topics for the LDC Atlas from this chapter. (See "Assignments" in the Syllabus.)
Conflict in Rwanda
shifting cultivation
Where people live/why?
unique phys. geog.
major rivers
Region: ..(select one)......
Nomadism
British colonies
French colonies
Portuguese colonies
Measures of development
mining
Conflict in Rwanda
Conflict in Liberia
Conflict in Sierra Leone
Other conflicts
Water Bodies
Lake Victoria
Indian Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
Rivers
Niger River
Zaire (Congo) River
Zambezi River
Orange River
Nile River
Blue Nile
White Nile
Land Areas
Madagascar
Kalahari Desert
Cape of Good Hope
Ethiopian Highlands
Congo Basin
the Sahel
the Sahara
Namib Desert
rift valleys
great escarpment
Countries
Angola /Benin /Botswana
Burkina Faso /Burundi /Cameroon
Central Afr.Republic /Chad /Congo
Equatorial Guinea /Ethiopia /Gabon
Gambia /Ghana /Guinea
Guinea-Bissau /Ivory Coast /Kenya
Lesotho /Liberia /Madagascar
Malawi /Mali /Mauritania
Mozambique /Namibia /Niger
Rwanda/ Senegal /Sierra Leone
South Africa/ Swaziland /Tanzania
Togo /Uganda /Zaire
Zambia /Zimbabwe /Eritrea
Nigeria /Somalia
Missing
de Blij: Chapter 6
|
R&P GEOG |
CULT GEOG |
ECON GEOG |
HIST GEOG |
|
274-276 |
280-287 |
287-290 |
276-280 |
1. Identify the criteria used to designate this realm and the regions within it. (R&P GEOG)
2. Locate the major features of Southwest Asia and North Africa on a map, including the countries, prominent physical regions, primary rivers, and major land and water bodies. (R&P GEOG)
3. Explain the three main religions of Southwest Asia and North Africa and the role each plays in the area today. Emphasize the different roles of Islam on the life and politics of its followers. Evaluate the relative strength of Arab nationalism today. (CULT GEOG)
4. Describe the impact of Western colonization the Middle East and North Africa and Russian colonization of Turkestan. Indicate the impact that colonization has on politics in these countries today. (HIST GEOG)
5. Explain some of the origins of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Also, describe the present status of the Arab/Israeli Peace Accord signed in Washington, DC. in October, 1993 and the issues which need to still be resolved today. (CULT GEOG)
6. Describe the role of ethnic groups and nationalism in this realm. Also, examine the devolutionary and balkanization forces in the following areas:
(1) Turkestan, (2) Tunisia or Algeria, (3) Afghanistan, (4) Iraq, (5) other (CULT GEOG)
7. Discuss the role of oil in the economic development of the region. (ECON GEOG)
8. Apply the measures of economic development to the region. (ECON GEOG)
|
Islam |
nation |
Listed below are some suggested topics for the LDC Atlas from this chapter. (See "Assignments" in the Syllabus.)
Conflict in Israel
Region:...(select one)......
Where people live/why?
The Kurds
Marsh Shiites
British colonies
French colonies
Italian colonies
Israeli-Palestinian peace?
Political problems in Algeria
The Nile
Nomadism
Measures of development
Monarchies
Aral Sea
Why include Turkestan?
Oil: Where and Effects?
Islam
Formation of Israel
Sunni and Shiite
Islamic Fundamentalism
Conflict in Afghanistan
Conflict in Turkestan
Conflict in Azerbaijan
Phys. Geog. of the Realm
Land Bodies
Atlas Mountains
Hindu Kush Mountains
Ethiopian Highlands
Zagros Mountains
Sahara Desert
Rub al Khali (desert)
Sinai Peninsula
Cyprus
West Bank
Gaza
Golan Heights
Rivers
Nile
Tigris
Euphrates
White Nile
Blue Nile
Water Bodies
Red Sea
Strait of Gibraltar
Persian Gulf
Mediterranean Sea
Aral Sea
Lake Nasser
Caspian Sea
Black Sea
Bosporous Straits
Countries
Afghanistan/ Algeria /Bahrain
Cyprus /Djibouti /Egypt
Eritrea /Iran /Iraq
Israel /Jordan /Kazakhstan
Kuwait/ Kyrgyzstan/ Lebanon
Libya /Morocco /Oman
Qatar /Saudi Arabia/ Somalia
Sudan /Syria /Tajikistan
Tunisia /Turkey /Turkmenistan
United Arab Emirates /Uzbekistan /Yemen
Missing
Study Guide: Tropical Africa by Tony Binns, pp.100-104
A Man's Day / A Women's Day
periodic market
tribe
Peace Corps
ugali
maize
1. To begin understanding how different life is in a developing country from life in the United States.
2. To recognize that our own experiences affect the way we view the developing world (i.e. often there isn't a "right" way to do something).
3. To think about the often times difficult role of women in the developing world.
1. What was your initial reaction to the slide show on Kenya?
2. What additional questions do you have?
3. Would you like to live as your instructor did in a developing country for a while? Why or why not?
pp.100-104 - Missing
Missing
- keep your Study Guide open to the Objectives, Vocabulary, and
other information
- pay close attention to the THEMES, again, see the Study Guide (p.
47)
- you should have already read the material (Intro, 8, 7, handouts),
if not READ!
- take notes as you read, see the Objectives in the Study Guide
AGAIN!
- read your class notes
- prepare study notes of each objective and vocabulary word
Remember, I do not stress simple memorization, but rather my exam questions will require the APPLICATION of the terms and concepts we have studied. In order to do this you do need some facts. These you get from the readings. But as you read, or review, try to fit the material into our four themes. Take notes that relate the readings to the themes and objectives. This should be work. Reading, if it is easy, really isn't learning.
The exam will have a variety of question types: Multiple Choice, Short Answer, Essay, Map Work, Lists, Definitions, etc. Those listed here are JUST EXAMPLES. Do not just prepare answers to them. These should be used as a guide so that you can see if you are prepared. If you could not answer SIMILAR types of questions on DIFFERENT issues covered in class then you are NOT ready. If all you do is look up the answers to these questions you will not pass. If, AFTER STUDYING all the material, you could answer all of these questions easily, you are probably ready.
REGIONAL GEOGRAPHY
1. What are the five "regional criteria"?\
2. Given the hypothetical data and maps of Harperland below:How
would you
divide these countries into realms?
Explain and justify your answer by applying the regional criteria using the maps and data provided.
3. Explain what could be "geographic" about a course entitled "The Geography of NFL Football Teams"?
(What is geography? What do geographers study?)
4. Why are all (almost) regional boundaries "transition zones"?
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY
5. Briefly describe A Climates (or B, C, D, H).
6. Locate the world's three main population clusters on a map. Use the "5 Reasons why people live where they do" to explain why so many people live in these clusters.
7. Given the hypothetical data and maps of Harperland below, indicate where you think most people would live and explain why.
ECONOMIC GEOGRAPHY
8. What does LDC stand for? (MDC?)
9. What are the 1st world, 2nd world, and the 3rd world?
10. Why is the term "Third World" used very little now?
11. Which of the following is a Primary Economic Activity? (Secondary? Tertiary? Quaternary?)
12. What are the "Measures of Economic Development"?
13. For each measure of economic development:
What is high? low?
What indicates an LDC? MDC?
Explain.
14. Given the hypothetical data and maps of Harperland below: Are these countries a MDCs or LDCs? Justify your answer.
15. Why is GDP (or GNP) not a good measure of economic development or of a country's standard of living?
16. Of the developing realms, which is the most urbanized? least urbanized? most developed? least developed?
ECONOMIC CHANGE
17. Define regional complementarity and give an example.
18. List the characteristics of Market Economies and of Command Economies.
19. List the costs and benefits of Market Economies and of Command Economies.
20. List the policies included in Structural Adjustment Programs (SAPs).
21. What are Structural Adjustment Programs and why are so many countries undertaking them?
22. How do most of the people living in LDCs make a living?
23. What is efficiency?
CULTURAL GEOGRAPHY
24. Define culture, list its components, and give examples of its components?
25. Explain the differences between state, nation, nation-state, and multinational state. citing examples.
26. Give real-world examples of: balkanization, irredentism, and devolution.
27. List several centrifugal forces and centripetal forces found in many LDCs.
28. Compare and contrast acculturation and transculturation, giving examples of each.
29. How has the cold war led to political instability in some LDCs? Give examples.
HISTORICAL GEOGRAPHY
30. Who was the major colonial power in South America? South Asia? Middle America?
31. Name a colonial power and the present-day country they colonized in Southeast Asia. in North Africa and Southwest Asia. in Sub-Saharan Africa.
32. What is a culture hearth?
33. Where was the Ottoman Empire and when did it collapse?
34. List 5 effects of colonization and give a real-world example of each.
SUB-SAHARAN AFRICA
35. Apply the "'Regional Criteria" to the border between North Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa. Why did the author of the textbook divide Africa into two different realm?
36. Apply the "Regional Criteria" to one region (or 2,3,4) of Sub-Saharan Africa.
37. Where are population densities the highest in Sub-Saharan Africa and why? (Where do people live and why?)
38. Discuss the UNIQUE physical geography of Africa.
39. What is the process responsible for the escarpments, elongated lakes and lack of major mountain chains, that we find in Sub-Saharan Africa? Explain.
40. Give a example from Sub-Saharan Africa for each of the following and explain:
balkanization, irredentism, centrifugal force, centripetal force, nation, state, nation-state, multinational state, cold war, coup d'etat
41. What is shifting cultivation, where does it occur, and why does it occur there?
42.. What problems are associated with shifting cultivation?
43. Explain briefly the recent political history of South Africa. Use the following term correctly in your explanation: apartheid, homelands, African National Congress (A.N.C.), Afrikaner
44. Why are many people surprised at the actual size of Africa?
NORTH AFRICA AND SOUTHWEST ASIA
45. Discuss why the following terms have been applied to North Africa and Southwest Asia and state the problems with each of them.
The Dry World
The Arab World
The Muslim World (Islamic)
The Middle East
46. Select one (or 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) of the regions within North Africa and Southwest Asia and apply the "regional criteria" to explain who it is different from adjacent regions.
47. Briefly explain the 1948 origin of Israel and the current Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
48. Explain the current state of the Israeli-Palestinian Peace Accord.
49. Who are the Kurds?
50. Briefly describe the events of the 1990-91 Gulf War.
51. Locate on a map the three main areas where oil is found in North Africa and Southwest Asia.
52. List and briefly discuss the FOUR DIVISIVE FORCES mentioned in the textbook.
53. What culture hearth(s) was/were located in North Africa and Southwest Asia?
54. How is oil a "double edged sword"? (List the benefits and the problems encountered by the oil-rich states of North Africa and Southwest Asia.
55. Where do most people live in North Africa and Southwest Asia and why?
Measures of Economic Development
Country GNP/pers Pop growth Wkfce prim Urban pop Energy cons Road km Land area Deaths <1
Facland 21100 0.6 3 78 9542 6261876 83635 4.0
Stuudland 990 2.9 67 24 200 122000 94534 22.0
Adminstra. 1240 1.7 22 35 354 19857 15590 18.0
Grads 4400 1.0 18 55 1760 52264 9880 12.0
Flunk 320 3.6 76 18 78 10789 9356 25.0
GNP/pers GNP per capita
Pop growth Annual population growth rate (%)
Wkfce prim % of workforce in primary activities
Urban pop Urban population as a % of total population
Energy cons Energy consumption in kg per person
Road km length of road network
Land area total land area in square kilometers
Deaths <1 Deaths of children less than 1 year old out of 1000 live
births