|
|
|
The best way to review for exam 1 is to:
- Look up everything on this study guide in the book or instructor notes.
- Write down the definitions of all words listed.
- You may need to use the index at the back of the textbook and the vocabulary links at the end of the instructor notes.
- Find all figures either in the textbook or instructor notes and read all you can about them.
Also:
- read the assigned readings (you may want to take notes)
- read the Instructor notes for each week
- learn the vocabulary !!!
- study the maps and figures in the textbook and instructor notes; there will be maps and figures on the exam
- review the Required Activities
This "review" page is intended to narrow your studying as you prepare for taking the exam or retake.
MODELS
Seventeen geographic models were introduced in this unit.The EXAM REVIEW link on Blackboard will give you access to a "Practice Quiz on Geographic Models" and there is a summary of the geographic models discussed in this unit at the end of this exam 3 study guide [Review of Geographic Models].
Week 11 Development
Week 12 Agriculture
Week 13 Industry
Week 14 Services and Urban Patterns
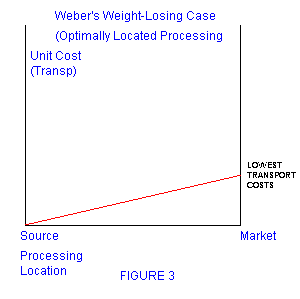
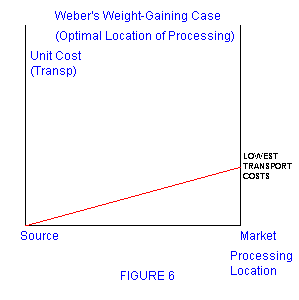
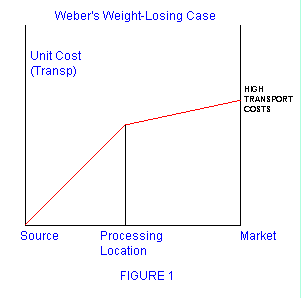
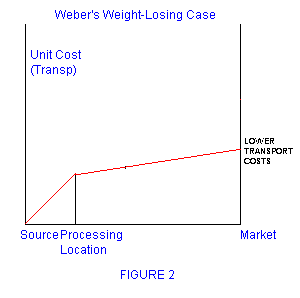
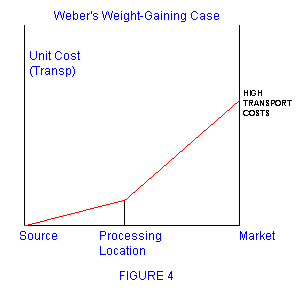
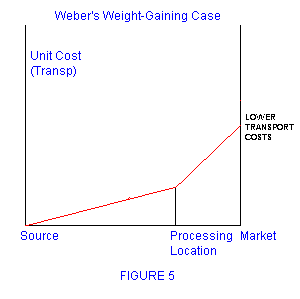
- Weber's model of industrial location
Assigned Readings for Unit 3:
- Week 11 Development
- Ch. 9 - Key Issues 1, 2 (review from week 1), and 4
- Ch. 14 - Key Issue 1
- Week 12 Agriculture
- Ch. 10 - All 4 Key Issues
- Week 13 Industry
- Ch. 11 - All 4 Key Issues
- Also: The Mystical Power of Free Trade
- Also: The Importance of German Immigration as a Locational Factor in the Illinois Brewing Industry: 1870 - 1920
- Week 14 Services and Urban Patterns
- Ch. 12 - Key Issues 2 and 4
- Ch. 13 - Key Issues 1 (only pp. 459-465 ), 2, and 4
- Don't forget the online videos, the instrructor notes, and the assigned "web Links"
WEEK 11 - DEVELOPMENT - Chapter 9 and 14
Define
- primary sector
- secondary sector
- tertiary sector
- fair trade
- structural adjustment programs
Textbook Figures
- 9-1
- 9-11
- 9-20
- 14-4
- 14-6
- 14-7
- 14-1
Other
- development through international trade approach
- online video "Sri Lanka vs. South Korea"
- Nationmaster
- Grameen Bank
- problems with using GDP per capita as a measure of average income
- what's included in the HDI
- the growing GDP per capita gap between MDCs and LDCs
- characteristics of LDCs and MDCs
- oil and development in the Middle East
- What is the less developed region with the highest percentage of people living in urban areas?
- International trade approach to development
Some other maps that may be seen in the exam
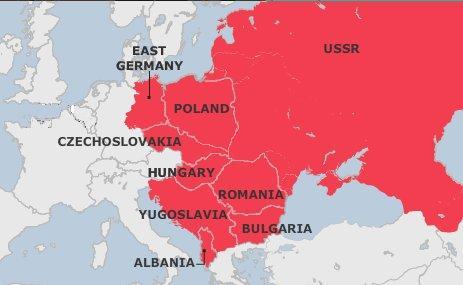
WEEK 12- AGRICULTURE - Chapter 10
Define
- winter wheat
- spring wheat
- truck farming
- swidden
- subsistence agriculture
- commercial agriculture
- transhumance
- double croppiing
- threshing
- winnowing
- agribusiness
- crop rotation
Textbook Figures
- 10-2
- 10-5
- 10-4 !!!
- 10-24
- 10-32
- 10-33
Other
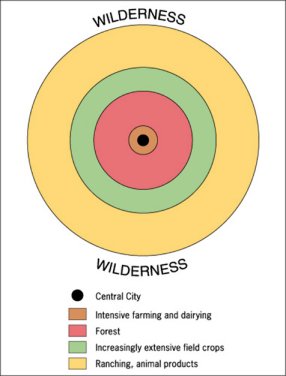
- Von Thunen Model !!! (see below for Review of Geographic Models)
- Agricultural Regions
- shifting cultivation
- pastoral nomadism
- intensive subsistence
- platation
- mixed crop and livestock
- dairy
- grain
- livestock
- Mediterranean
- commercial gardening and fruit
- grapes and wine production occur in which agricultural region?
- subsistence vs. commercial agriculture
- hunters and gatherers
- The first region to integrate seed agriculture with domestication of herd animals (Invention of Agriculture)
- Which type of agriculture occupies the largest percentage of the world's land area?
- The largest proportion of farmers in Asia practice which type of agriculture?
- Agricultural regions and Climate regions (compare the maps in figure 10-4) and know the climate types (A, B, C, D, E, and H)
- Intensive subsistence agriculture: wet rice dominant vs. wet rice not dominant
Some other maps and figures that may be seen in the exam
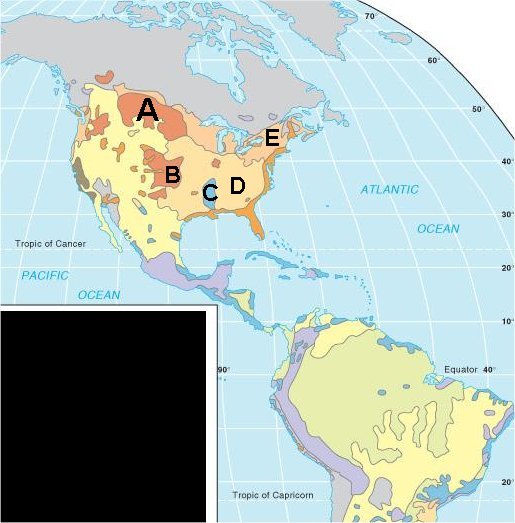
WEEK 13 - INDUSTRY - Chapter 11
Define
- industrial revolution
- cottage industry
- break-of-bulk point
- bulk gaining
- bulk reducing
- single market manufacturer
- perishable products
- site factors
- situation factors
- Fordist
- post-Fordist
Textbook Figures
- 9-3 (p. 276)
Other
- Do economists support free trade or trade restictions?
- What was one of the most important locational factors explaining the location of breweries in nineteenth century Illinois?
- The United States had the most breweries in which decade?
- The locational factors of the beer brewing industry tend to favor locating the brewery at the market. Which characteristics of the brewing process does NOT (i.e. which would favor brewing at the source of a resource)?
- world regions containing the most industry
- Europe's industrial areas
- North America's industrial areas
- East Asia's industrial areas
- Canada's industrial areas
- Russia's industrial areas
- the best location for a copper mill
- the best location for an auto factory (fabricated metal)
- ship, rail, truck, or air?
- the best location for aluminum manufacturing
- the best location for the textile industry
- Ural Mountain industrial area
Some other maps and figures that may be seen in the exam
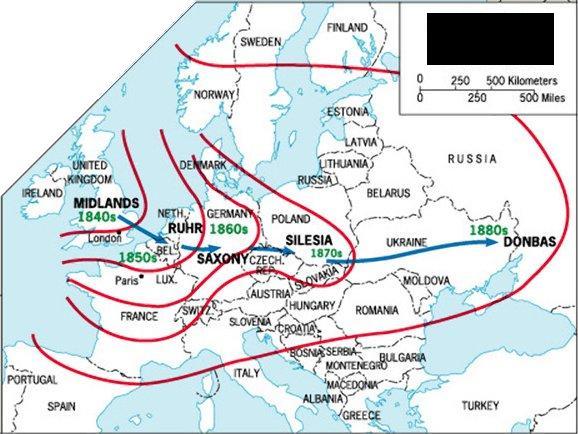
WEEK 14 - SERVICES AND URBAN PATTERNS - Chapters 12 and 13
Define
- density gradient
- urban sprawl
- urbanization
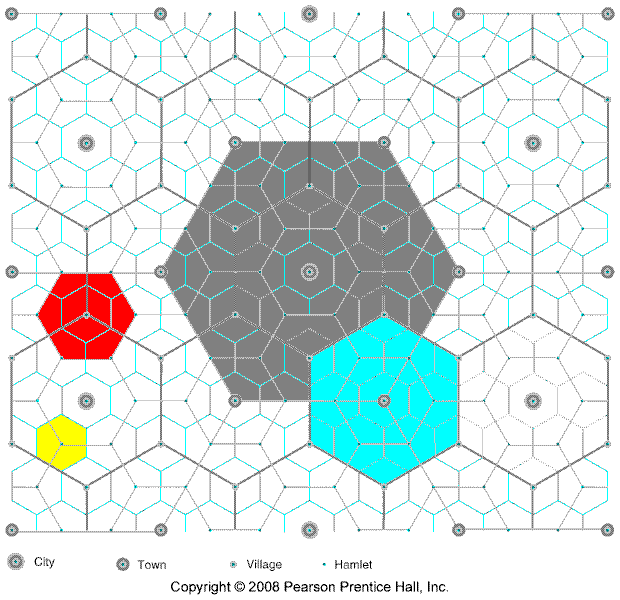
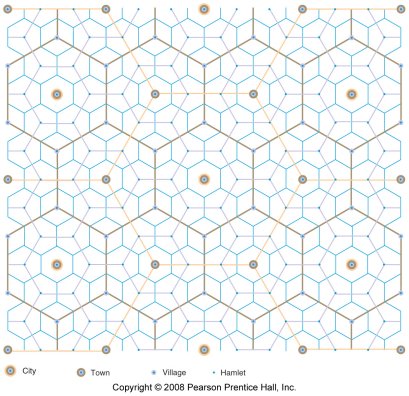
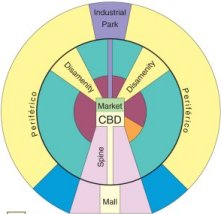
- central place theory
- edge city
- CBD
- threshold
- range
- gravity model
- median
- primate city
- primate city rule
- greenbelt
- squatter settlement
- factories moving to the suburbs
Textbook Figures
- 12-20
- 12-21
- 13-4
- 13-5
- 13-6
- 13-14
- 13-22
- 13-23
Other
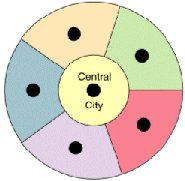
- Adam's model (stages of intraurban growth)
- Models of Urban Structure
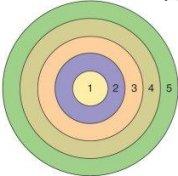
- concentric zone model
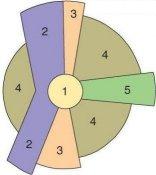
- sector model
- multiple nuclei model
- Multicentered/Peripheral model (pepperoni pizza)
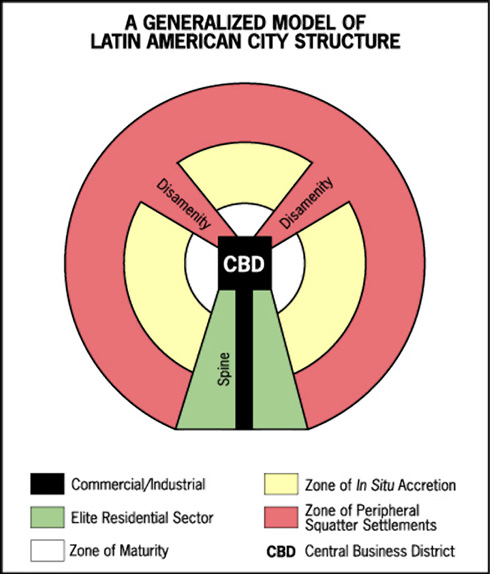
- model of a Latin American city
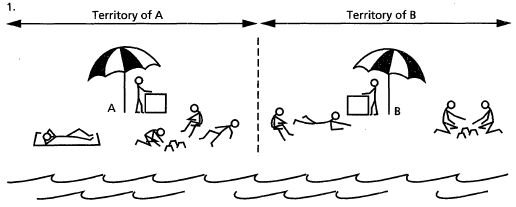
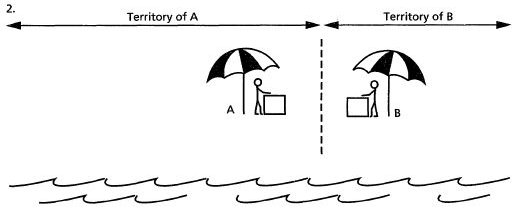
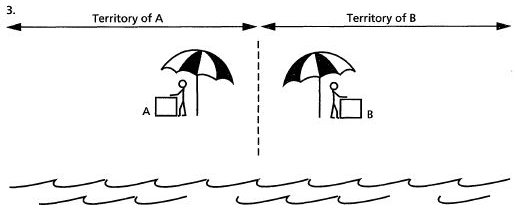
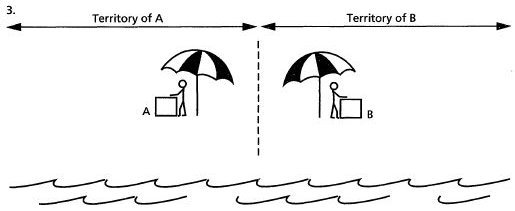
- Hotelling Model
- online video " Chicago: Farming on the Edge"
- Central Place Theory
- market area of a service
- hinterland
- which retail activities which tend to concentrate in the CBD?
- changes in the density gradient over time
- where do the urban poor live in US cities and in European cities?
- European cities
- Colonial cities
Some other maps and figures that may be seen in the exams
Geographic Models to know:
In this unit many "geographic models" were introduced. Models are simplifications of reality to help us better understand a concept. Models can be expressed in words, with drawings, or mathematically.
"A model is simply a representation of a real thing. You have seen
and used models in the past, like a globe which is a model of the
earth. Geographers construct models to analyze geographic processes
because the real object of study may be too large to examine, the
processes which created it operate over too long of a time frame, or
experimentation might actually harm or destroy it. For instance,
physical geographers use stream tables to investigate the impact of
hydrological processes on the earth. A stream table is more or less
like a shallow sink filled with earth material similar to the land
surface of interest. Water is applied to the material to see what
affect varying amounts of water have on the erosion of the surface.
Climate scientists use computer models, which are elaborate
mathematical models. Models can be as simple as a box and arrow
diagram showing the flows of energy between compartments of an
ecosystem to complex numerical statements of the impact of increasing
carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere on global temperature."
http://www.uwsp.edu/geo/faculty/ritter/geog101/textbook/essentials/models.html
Here is a list of the models introduced in this unit on economic geography:
|
Week 11 Development |
Week 12 Agriculture |
Week 13 Industry |
Week 14 Services and Urban Patterns |
|
Here is a BRIEF explanation of each model:
- Week 11 Development
- Development Through
Self-Sufficiency
- sometimes called the "balanced-growth", "import substitution", and "infant industry"
- Policies:
- to promote self sufficiency and development LDCs would erect trade barriers to limit imports into their country
- this then would reduce competition and result in higher prices, and higher profits, for domestic industries which could then grow creating jobs
- governments may also put certain restrictions on
domestic industries
- preventing them from exporting goods
- regulating their prices, expansion plans, hiring, etc.
- sometimes the government would need to subsidize (i.e. give money to) companies that were not profitable
- also common was government ownership of certain industries like communications (phone, Television, and radio companies), transportation (airlines), and power companies
- How they restricted trade:
- tariffs - taxes on imported items making them more expensive than domestically produced goods
- quotas - limits on the quantity of goods that can be bought from other countries (imported)
- licenses - requiring a license before goods can be imported then restricting the number of licenses
- Problems with the Self-sufficiency Alternative
- inefficiency - without competition there were no
incentives resulting in
- higher production costs
- low product quality
- higher prices
- out of date factories and products
- large government bureaucracy was needed to implement
the program resulting in
- abuse and corruption
- higher costs
- illegal activity (black market) to avoid government regulation
- waste of resources in an attempt to get around the regulation
- inefficiency - without competition there were no
incentives resulting in
- Summary:
- The self sufficiency approach to development wasted a lot of resources and resulting in LESS being produces with the resources available limiting development.
- Therefore most countries have switched to the international trade approach
- a few countries (Venezuela and Bolivia come to mind) have recently reverted back to the self sufficiency approach. Most economists expect the policies to fail and the standards of living to drop, but Venezuela's crude oil reserves have delayed the decline
- Development Through International
Trade
- What is it:
- relies on countries to SPECIALIZE in producing those products that they may be better at producing and then TRADING with other countries for products that they are not good at producing
- for example if a country has a lot of unskilled labor it may specialize in labor-intensive industries like textiles (clothing) or assembly, importing the raw material and exporting the finished product
- then, according to Rostow's model, the technology will diffuse to other industries (the drive to maturity stage) and more and more industries will experience rapid growth as well
- This is similar to what YOU are doing in your
personal lives and why you are going to college
- Imagine if you decided to become rich by being self-sufficient - you produced all things for yourself and did not buy (trade) anything. You grew your own food, built your own house, made your own clothes, cars, cell phones, computers, calculators, etc. WHAT WOULD YOUR LIFE BE LIKE?
- So what are you doing? You have decided to get an education and specialize in one career where you only do one thing, sell it to those who want it (like your employer), and you buy (trade) the products that you want. As a result of you specializing and trading, your standard of living will be much higher than if you sought to be self-sufficient and do everything for yourself
- Examples of the International trade Approach
- When most other countries were stagnating using the self-sufficiency approach, two groups of countries located in East and Southeast Asia and in the Middle East chose the development through trade approach with significantly better results
- The Four Asian Dragons (sometimes called the "Asian
Tigers")
- South Korea, Taiwan, Singapore, Hong Kong
- all had few natural resources
- concentrated on producing just a few manufactured goods, importing the materials necessary and using their low cost labor
- resulting in rapid economic growth as other industries entered Rostow's takeoff stage and in the labor force becoming more skilled and then receiving higher wages
- See our Online Video: "Sri Lanka vs. South Korea"
- Petroleum-rich Arabian Peninsula states
- unlike the Asian Tigers (Dragons), the Arabian Peninsula states had an important natural resource - oil
- using their oil revenues these states have invested in economic infrastructure (housing, highways, ports, universities) and in developing additional industries (petrochemicals, steel, aluminum)
- In Dubai, in the United Arab Emirates, in the
Middle Eastern desert, there is even an indoor snow
skiing hill!
See: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DycMJc-Ow-E
- Problems with the International Trade Alternative
- As we can see in our own economy here in the U.S.,
the capitalist / international trade approach doesn't
automatically make everyone rich, there are some problems
- uneven resource distribution
- periodic market stagnation
- increased dependence on MDCs, or on other countries in general
- unequal distribution of income - within a country some people get richer faster, some people advance more slowly
- As we can see in our own economy here in the U.S.,
the capitalist / international trade approach doesn't
automatically make everyone rich, there are some problems
- Recent Triumph of the International Trade
Approach
- Most countries have switched to the international
trade approach to development
- world trade has tripled in the last 25 years
- world wealth has doubled in the last 25 years
- India is a good example (and Sri Lanka)
- "Countries like India converted from self-sufficiency to international trade during the 1990s for one simple reason - overwhelming evidence that international trade better promoted development" (p. 297)
- Most countries have switched to the international
trade approach to development
- What is it:
- Rostow's Development Model
- a five stage model of development
- TRADITIONAL SOCIETY - traditional subsistence agriculture dominates
- PRECONDITIONS FOR TAKEOFF - an elite well educated group initiates innovative economic activities as the country invests in new technology and infrastructure
- TAKEOFF - rapid growth is generated in a limited number of economic activities which achieve technical advances while the rest of the economy remains in traditional activities
- DRIVE TO MATURITY - the technology of the few take industries diffuses to a wide variety of industries as modernization diffuses throughout the economy
- AGE OF MASS CONSUMPTION - the economy shifts from heavy industry (steel and energy) to producing consumer goods
- sometimes combined with the international trade model
- a five stage model of development
- Development Through
Self-Sufficiency
- Week 12 Agriculture
- Week 13 Industry
- Week 14 Services and Urban Patterns
The EXAM REVIEW link on Blackboard will give you access to a "Practice Quiz on Geographic Models".
INSTRUCTOR:
E-Mail instructor: mhealy@harpercollege.edu
Office: J-262
Phone: 847-925-6352
Home: 815-728-1571
Cell: 815-861-7265