|
Home
Syllabus
Schedule
Assignments
Online Lectures
Discussion
Forum
Review
Textbook
Website
|
ECO 212 ONLINE! does have a comprehensive final exam.
There will be 80 multiple choice questions and NO extra
credit essay. Students always ask me for suggestions on how
to study for the final. Hopefully, you have been preparing
for the final throughout the semester.
There are some chapters that will be more important than
others. These are usually the chapters with the new models
(i.e. graphs) and concepts. You can probably figure out
yourself which chapter they are, but here is a list:
- chapter 2: production possibilities graph
- chapter 3: supply and demand graph
- chapter 6 and 20: using the production possibilities
graph to determine comparative advantage
- chapter 11: AD/AS graph
- chapter 7 calculating GDP,
- chapter 12: calculating and using the
multipliers
- chapters 12, 14, 15: shoeing how monetary policy
policy works on the set of 3 graphs
Anything covered during the semester can be on the final
exam, but there are some topics that are more likely to
appear there.
Chapter 1
- What is structural adjustment, what are its policies,
and why are countries doing it?
- What is economics? What role does scarcity play?
- What are the "5 Es" of economics and how does each
one reduce scarcity?
- What are the 4 factors of production (types of
resources)?
Bonus Web Chapter
- Compare command and market economies
- What are the "coordinating problem" and the
"incentive problem" found in command economies?
Chapter 4
- What are the characteristics of market (capitalist)
economies?
- What is the "invisible hand" and how does it promote
efficiency?
- Understand the important role of prices in a market
economy
- Understand the connection between the market economy
and the 5Es
Chapter 2
- What is the production possibilities table/graph
(PPC)? What does it show?
- What are the assumptions behind the PPC?
- How can we demonstrate the following using the PPC?
- the necessity of choice
- opportunity costs
- law of increasing costs
- unemployment
- productive inefficiency
- economic growth (EG)
- present choices, future possibilities
- optimum product mix?
- Give two definitions of EG
- Understand the simple circular flow model
Chapter 3
- THIS CHAPTER IS IMPORTANT
- Be able to define and graph demand and supply .
- Know
- the law of demand
- the law of supply
- market demand
- market supply
- determinants of demand
- determinants of supply
- Know the difference between a change in quantity
demanded (supplied) and a change in demand (supply)
itself
- Be able to use the demand and supply graph , AND
THEIR DETERMINANTS, to analyze why equilibrium prices
change
Chapter 5
- No questions from chapter 5 pp. 84-89 will be on the
final exam
Chapter 6 and 20
- Know the advantages and disadvantage of trade
- Be able to find which country has a comparative
advantage using the production possibilities table and
graph
- Be able to calculate the gains from trade when
countries specialize 100%
- What are the types of trade barriers?
- KNOW THAT THE COSTS OF TRADE BARRIERS ARE GREATER
THAN THEIR BENEFITS
- Understand the arguments used to support the use of
trade barriers AND the problems associated with each
argument
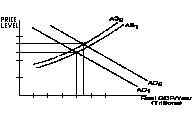
Chapter 11
- THIS CHAPTER IS IMPORTANT
- Know the business cycle and what happens to UE, IN,
and EG in each stage
- Define AD, know why is it downward sloping, and know
the determinants
- Define As, know why is it has the shape that it does,
and know the determinants
- Be able to use the AD and AS graph , AND THEIR
DETERMINANTS, to analyze why equilibrium real national
output and the price level change, AND relate those
change to UE, IN and EG.
- Know the definition and tools of the following:
stabilization policies"
- demand management policies
- fiscal policy
- monetary policy
- supply-side policies
Chapter 5
- Have a general understanding of federal, state, and
local government's sources of revenue and
expenditures
- Be able to calculate the marginal income tax rate and
the average income tax rate
Chapter 8
- What is UE?
- who is included?
- who is not?
- What is full employment?
- What are frictional UE, structural UE, and cyclical
UE?
- What is the "full employment rate of unemployment" or
the "natural rate"?
- What are the costs of UE?
- What is inflation (IN)?
- What is a price index?
- What is the rule of 70?
- Be able to calculate the inflation rate using price
index numbers
- Know demand-pull inflation and cost-push
inflation.
- What are the effects of inflation?
For chapters 7, 17, and 22 you may want to see: http://www.harpercollege.edu/mhealy/eco212/review/e2u2rev.htm
Chapter 7
- Define GDP
- What are the problems associated with using GDP as a
measure of economic welfare?
- Be able to calculate:
- GDP using the expenditures approach
- NI using the income approach
- NDP (net domestic product).
- real GDP using a price index
Chapter 17
- Know the difference between the two (or three) types
of economic growth
- increasing our ABILITY to produce or our Potential
output (increasing AS and the PPC)
- increasing real GDP or ACHIEVING our potential
output (increasing AD)
- increasing GDP per capita
- Have a general understanding of what has accounted
for growth in the United States over the last few
decades
Chapter 22
- Know the characteristics of the less developed
countries (called "developing countries" or "DVCs" in
our textbook)
- How does population growth affect the growth in GDP
per capita?
- What is the "vicious cycle" and how does population
growth affect it?
- Understand the "trade vs. aid" issue
Chapter 12
- THIS CHAPTER IS IMPORTANT
- if: equilibrium GDP is $400 billion, the full
employment level of GDP is $500 billion, and MPC is 0.8,
what change in government purchases is needed to achieve
full employment?
- be able to define and calculate MPC, MPS, APC, APS
using data from a table or from a graph of consumption
and income
- Understand how/why the multiplier effect works (i.e.
the rationale behind how it works)
- understand each of the multipliers listed at:
http://www.harpercollege.edu/mhealy/eco212/lectures/fiscpol/multiply.htm
- What are "built-in stabilizers" and how do they
work?
- What is the full-employment budget?
- What in the timing problem of fiscal policy? Know:
- recognition lag
- administrative lag
- operational lag
- What is "crowding out"?
- What is the "net export effect"?
Chapter 13
- What is money, liquidity, M1, money demand,
transactions demand, asset demand?
- What is not money?
- Know the money market graph
- Have a general understanding of the structure of the
Federal reserve system
- What are the functions of the FED?
Chapter 14
- THIS CHAPTER IS IMPORTANT
- Using the balance sheet of a single bank or the
banking system be able to calculate:
- total reserves
- required (legal) reserves
- excess reserves
- What is fractional reserve banking and how do banks
"create" money?
- Be able to calculate the "money multiplier"
- If $10 cash is deposited into a checking account at a
bank and the RR is 0.2 how much can this bank legal loan
out and how much money can be created by the banking
system?
- See the study guide problems !!!!
Chapter 15
- Know the "Keynesian Cause-Effect Chain of Monetary
Policy":
- 1. A change in the Fed tools CAUSES
- 2. a change in excess reserves CAUSES
- 3. a change in the money supply CAUSES
- 4. a change in the interest rate CAUSES
- 5. a change in investment CAUSES
- 6. a change in aggregate demand CAUSES
- 7. a change in real GDP and a change in the price
level CAUSES
- 8. a change in unemployment and/or inflation
- Know how to use these graph to illustrate the effects
of monetary policy:
- Understand how EACH of the three tools of monetary
policy (OMO, RR, and the DR) can be used to change the
money supply and hence UE, IN, and EG
- What are the strengths and shortcomings of monetary
policy?
FINAL NOTE:
Questions may appear on the exam that are not on this
final exam review list, but probably not many, if any.
GOOD LUCK.
|