Step 2: FNB makes loan equal to its excess reserves
Step 3: Loan is spent, deposited in SNB, and the check clears
Major Point: An initial increase in funds available to the banking industry results in a MULTIPLE increase in the money supply.
Three Step Process per Round:
Given:
Required Reserve Ratio = 20%FNB = First National Bank
SNB = Second National Bank
TNB = Third National BankER = excess reserves
All banks initially have no excess reserves
Banks make loans equal to their excess reserves
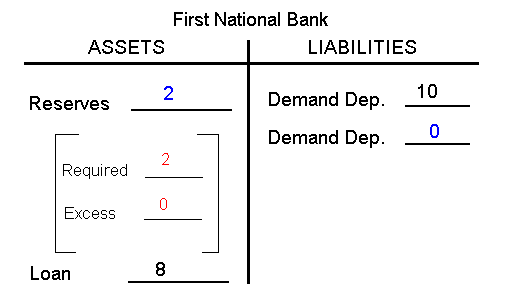
$10 cash is deposited in a checking (DD) account at FNB
Show:
The CHANGES in the balance sheets of each bank as a result of this $10 cash deposit and the increased loan making ability of the banks.
Round One
Step 1: $10 deposited in FNBStep 2: FNB makes loan equal to its excess reserves
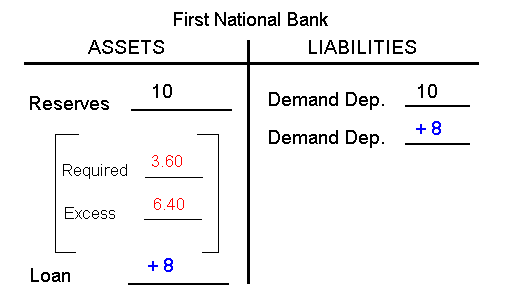
Step 3: Loan is spent, deposited in SNB, and the check clears
Round Two
Step 1: Check from round one deposited in SNBStep 2: SNB makes loan equal to its excess reserves
Step 3: Loan is spent, deposited in TNB, and the check clears
Round Three
Step 1: Check from round two deposited in TNB
How much money was created in round one? ____$ 8____How much money was created in round two? ____$ 6.40_
How much money can be created in round three? ____$ 5.12_
Deposit Expansion Multiplier = 1 / Required Reserve Ratio
(also called Money multiplier)Money Multiplier = total increase in money supply / initial excess reserves
What is the money multiplier? _____5______
What is the maximum total increase in the money supply that can occur as a result of the initial $10 cash deposit? ____$ 40_____
What are the limitations on this money creation process?
_____1) banks may hold ER ____________________________2) people may hold money_________________________
_____3) the required reserve ratio_______________________