TOPICS
- Stabilization
Policies
- Fiscal Policy
- Monetary Policy
- Supply-side policy
- AS/AD in the Long Run
- More Practice with the AS/AD Model: Economic history of
the U.S.
- The Phillips Curve
OUTCOMES
Differentiate between
expansionary and contractionary fiscal policy and
recognize the conditions on an AD/AS graph for
recommending an expansionary or contractionary
policy.
Differentiate between easy
(expansionary) and tight (contractionary) monetary policy
and recognize the conditions on an AD/AS graph for
recommending an expansionary or contractionary
policy.
Know how a change in the money
supply is transmitted to a change in AD
[ MS MS
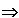
 interest
rates interest
rates 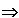
 I
I 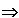
 AD] AD]
Supply-side policies and
equilibrium output
Explain long run adjustments to
changes in AD and why the long-run aggregate supply curve
is a vertical line (LRAS).
The first paragraph of
chapter 18 says:
"During
the early years of the Great Depression, many
economists suggested that the economy would correct
itself in the long run without government
intervention. To this line of thinking, economist
John Maynard Keynes remarked, “In the long run
we are all dead!”
Using the AS/AD model
explain and show how an econmy will "correct
itself" if it has high unemployment.
Using the AS/AD model explain and show how an
economy will "correct itself" if it has high
inflation.
Use the AD/AS model (graph) to
explain the economic history of the United States in the
past hundred years including the "Great Depression" of
1929-1939 and the "Great Recession" of
2007-2009.
The Phillips Curve
|