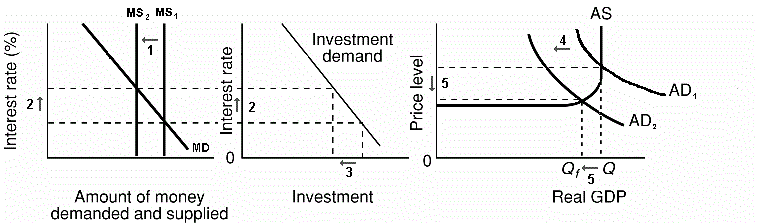
1. occurs when the Fed tries to increase money supply by
expanding excess reserves in order to stimulate the economy.
2. GOAL: to reduce unemployment
3. The Fed will enact one or more of the following
measures.
a. The Fed will buy securities.
b. The Fed may reduce reserve ratio, although this is
rarely changed because of its powerful impact.
c. The Fed could reduce the discount rate, although
this has little direct impact on the money supply.
4. Expansionary or easy money policy: The Fed takes steps to
increase excess reserves, banks can make more loans increasing the
money supply, which lowers the interest rate and increases
investment which, in turn, increases GDP by a multiple amount
of the change in investment.

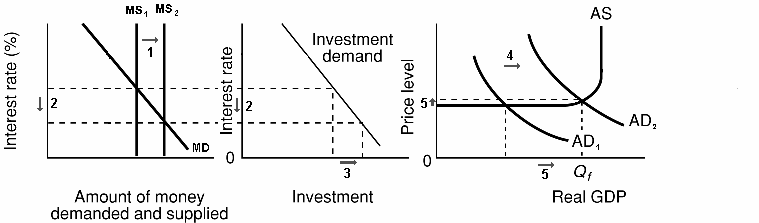
1. occurs when Fed tries to decrease money supply by
decreasing excess reserves in order to slow spending in the
economy during an inflationary period.
2. GOAL: to reduce inflation
3. The Fed will enact one or more of the following
policies:
a. The Fed will sell securities.
b. The Fed may raise the reserve ratio, although this
is rarely changed because of its powerful impact.
c. The Fed could raise the discount rate, although it
has little direct impact on money supply.
4. Contractionary or tight money policy is the reverse of an
easy policy: Excess reserves fall, the money supply decreases,
which raises interest rate, which decreases investment, which, in
turn, decreases GDP by a multiple amount of the change in
investment.