|
FED
|
I. Preview / Review
A. The following figure and graphs illustrates what we have already done in chapters 9, 11, 12, 13, and 14, and what we will be doing in chapter 15
FED
TOOLS ![]()
![]() ER
ER![]()
![]() MS
MS
![]()
![]() Int.
Rates
Int.
Rates![]()
![]() I
I
![]()
![]() AD
AD
![]()
![]()
![]() real
GDP
real
GDP ![]()
![]() UE
UE
![]() Price
Level
Price
Level
![]()
![]() IN
IN![]() OMO
OMO![]() DR
DR
![]() RR
RR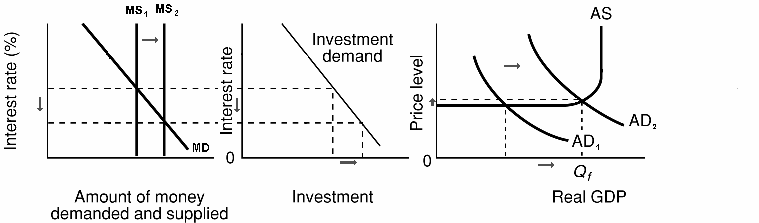
B. Chapters 11 and 12
- a change in the money supply (
MS) causes a change in interest rates (
Int. Rates)
- a change in interest rates (
Int. Rates) results in a change in Investment (
I)
- a change in Investment (
I) will change Aggregate Demand (
AD)
- a change Aggregate Demand (
AD) will change real GDP and therefore unemployment (
real GDP
UE)
- change Aggregate Demand (
AD) will also change the price level, assuming we are in the intermediate range of the AS curve, and therefore it will also change inflation (
Price Level
IN). See the figure below and the graph.
FED
TOOLS ![]()
![]() ER
ER![]()
![]() MS
MS
![]()
![]() Int.
Rates
Int.
Rates![]()
![]() I
I
![]()
![]() AD
AD![]() OMO
OMO
![]() DR
DR
![]() RR
RR
![]()
![]()
![]() real
GDP
real
GDP ![]()
![]() UE
UE
![]() Price
Level
Price
Level
![]()
![]() IN
IN
C. Chapter 13
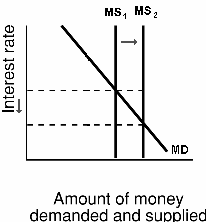
we learned how a change in the money supply (
MS) creates a change in interest rates (
Int. Rates).
See figure above and the graph below.
FED
TOOLS ![]()
![]() ER
ER![]()
![]() MS
MS
![]()
![]() Int.
Rates
Int.
Rates![]()
![]() I
I
![]()
![]() AD
AD
![]()
![]()
![]() real
GDP
real
GDP ![]()
![]() UE
UE
![]() Price
Level
Price
Level
![]()
![]() IN
IN![]() OMO
OMO
![]() DR
DR
![]() RR
RR
D. In chapter 9 of the textbook1. Investment consists of spending on new plants, capital equipment, machinery, inventories, construction, etc.2. The expected rate of return is found by comparing the expected economic profit (total revenue minus total cost) to cost of investment to get the expected rate of return. The text's example gives $100 expected profit on a $1000 investment, for a 10% expected rate of return. Thus, the business would not want to pay more than a 10% interest rate on investment. Remember that the expected rate of return is not a guaranteed rate of return. Investment carries risk.
3. The real interest rate, i (nominal rate corrected for expected inflation), determines the cost of investment.
a. The interest rate represents either the cost of borrowed funds or the opportunity cost of investing your own funds, which is income forgone.b. If real interest rate exceeds the expected rate of return, the investment should not be made.
4. Investment demand schedule, or curve, shows an inverse relationship between the interest rate and amount of investment.
a. As long as expected return exceeds the interest rate, the investment is expected to be profitableb. Figure 9-5 shows the relationship when the investment rule is followed. Fewer projects are expected to provide high return, so less will be invested if interest rates are high.
Figure 9.5
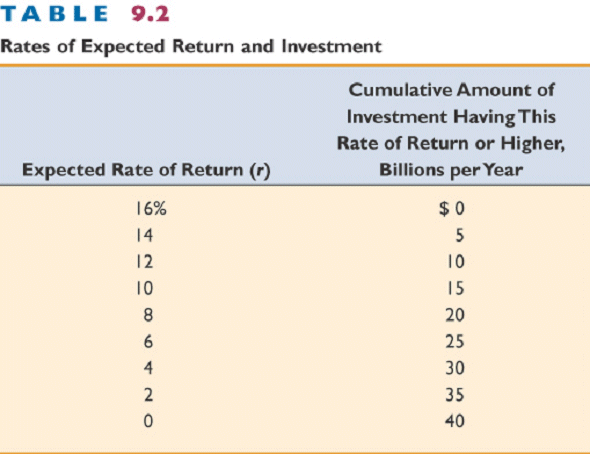
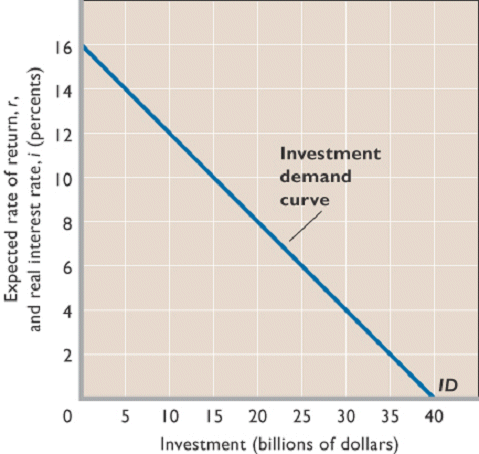
5. graph
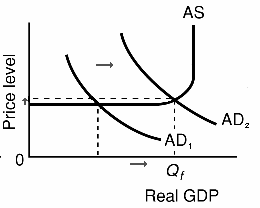
E. Put all the chapter graphs together: IF the MS increases:
FIRST: Chapter 13 THEN: Chapter 9 FINALLY: Chapters 11 and 12 If the MS increases: If the interest rates decline: If investment increases:


F. Chapter 14:
- How money is created to increase the money supply (MS)
ER

MS
FED
TOOLS ![]()
![]() ER
ER![]()
![]() MS
MS
![]()
![]() Int.
Rates
Int.
Rates![]()
![]() I
I
![]()
![]() AD
AD![]() OMO
OMO
![]() DR
DR
![]() RR
RR
![]()
![]()
![]() real
GDP
real
GDP ![]()
![]() UE
UE
![]() Price
Level
Price
Level
![]()
![]() IN
IN
G. What is left to learn?1. Chapter 15 - How the Fed controls the money supply: FED TOOLS
- open market operations (OMO)
- changing the discount rate (DR)
- changing the require reserve ratio (RR)
FED
TOOLS
![]()
![]() ER
ER![]()
![]() MS
MS
![]()
![]() Int.
Rates
Int.
Rates![]()
![]() I
I
![]()
![]() AD
AD![]() OMO
OMO
![]() DR
DR
![]() RR
RR
![]()
![]()
![]() real
GDP
real
GDP ![]()
![]() UE
UE
![]() Price
Level
Price
Level
![]()
![]() IN
IN
2. HERE IT ISIf there is HIGH UNEMPLOYMENT in the economy, the appropriate monetary policy policy and its effect illustrated on our graphs would be:
FIRST: Chapters 14 and 15 SECOND: Chapter 13 THIRD: Chapter 9 FINALLY: Chapters 11 and 12 To increase the MS the fed must increase the ER of
banks. Then banks could make more loans and create more
money. To do this they would use an easy money
policy. Easy Money Policy: If the MS increases: If the interest rates decline: If investment increases:



![]() DR)
DR)![]() RR)
RR)
If there is HIGH INFLATION in the economy, the appropriate monetary policy policy and its effect illustrated on our graphs would be:
FIRST: Chapters 14 and 15 SECOND: Chapter 13 THIRD: Chapter 9 FINALLY: Chapters 11 and 12 To decrease the MS the Fed must decrease the ER of
banks. Then banks could make FEWER loans and create more
money. To do this they would use a tight money
policy. Tight Money Policy: If the MS decreases: If the interest rates increase: If investment increases:
![]() DR)
DR)![]() RR)
RR)