|
|||||
|
|||||
DAILY SCHEDULE OF ASSIGNMENTS: Click on date for reading and video assignments.
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Reading: Videos: To watch 5 minute video: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
![]()
Extra Videos
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra Videos
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra
Reading: Videos: Poland: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
![]() (A free
registration is required for first time
users)
(A free
registration is required for first time
users)
Extra Videos
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra Videos
|
|
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
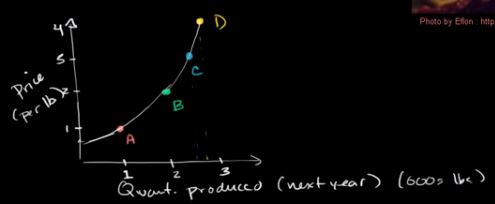
Extra Videos
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra Videos
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
http://www.cnn.com/ALLPOLITICS/time/1999/12/06/free.trade.html
Questions # 1, 3, 4, 8-12, 14 Problems 1, 2, 3
Extra Videos
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra Videos
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice: Chapter 12 Chapter 6
Extra Videos
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra Videos
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra Videos
Reading: Ch. 7: "GDP Price Index," pp. 141-142 Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra Videos
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra Videos:
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra Videos:
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
KEY GRAPHS
Extra Videos:
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra Videos:
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
KEY GRAPHS:
Extra Videos:
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra Videos:
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
KEY GRAPHS
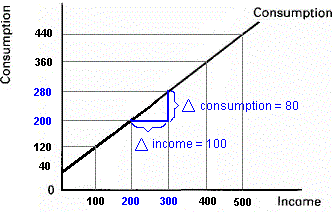
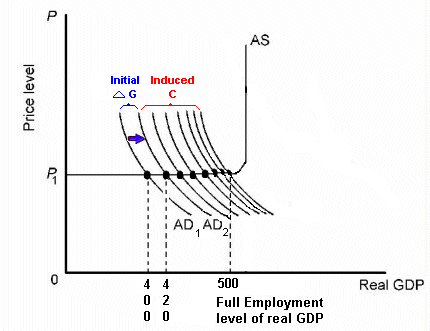
Extra Videos:
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
KEY GRAPHS

Extra Videos:
Reading: Videos: Outcomes / Must Know: Practice:
Extra Videos:
VIDEO SOURCES: YouTube ACDCLeadership Macroeconomics Videos Many students like these videos. I believe that "Mr.
Clifford " began making these videos for his AP Economics
students. I have watched many, but not all, of these videos
and I usually like the way that he covers the topics. He
does go quite fast, so the videos may be better for
review than for an initial introduction to the
topics. Note that his "units" do not match our units and he
may cover more than we do in some areas but not all that we
do in other areas.
Macroeconomics
Playlists
TOPICS / LESSONS: Click on lesson number for assignments.
Unit 1: ECONOMICS and GLOBALIZATION
Unit 2: INTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICS
Unit 3: MACROECONOMIC POLICY