TOPICS
- Positive
Externalities
- Public Goods
- Tragedy of the Commons
Market Failure: positive
externalities (also called external benefits or spillover
benefits)
define positive
externalities (external benefits or spillover
benefits)
give examples of positive
externalities
use the MSB=MSC model to show the
effects on allocative efficiency of positive
externalities
what can the government do to
correct the market failure caused by positive
externalities and show the effects of these policies on
the MSB=MSC model
Demand
is usually equal to MSB, but when there are positive
externalities the demand curve is to the left of the MSB
curve. Why?
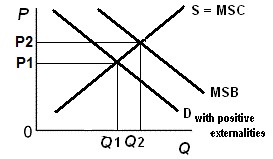
Are
positive externalities (spillover benefits) good or bad
for society? Why or why not?
Market Failure: Public
Goods
define "public goods
(public goods are non-exclusive and
non-rival)"
give examples of public goods and
explain why they are public goods
define private (exclusive) goods"
and give examples
define "rival goods" and give
examples
what is the "free rider
problem"?
explain how to derive the demand
curve for public goods
what effect do public goods have
on allocative efficiency?
what can the government do to
correct for the market failure of public
goods?
Why are public schools, public
parks, and public libraries NOT "public goods"? If they
are not public goods then why does the government produce
them?
Market Failure: Tragedy of the
Commons
what is the Tragedy of
the Commons (common access resurces are non-exclusive,
but rival)
how does the tragedy of the
commons affect allocative efficiency?
what can be done to better achieve
allocative efficiency when there is a tragedy of the
commons?
|