|
Click on the links above to learn how
to do these problems.
CALCULATE Ed USING MIDPOINTS
FORMULA
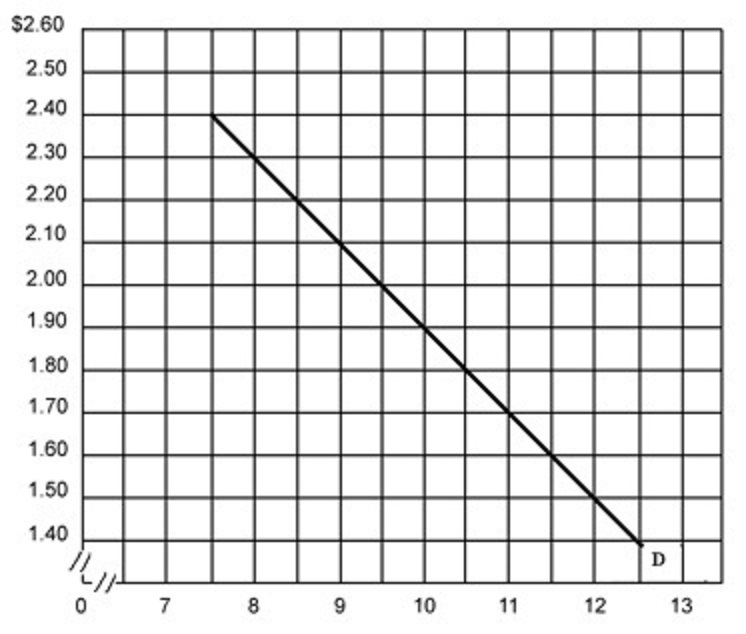
Calculate the price elasticity of
demand between a price of $2.40 and a price of $2.30
using the midpoints formula and interpret the
coeficient.
PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND AND
TOTAL REVENUE
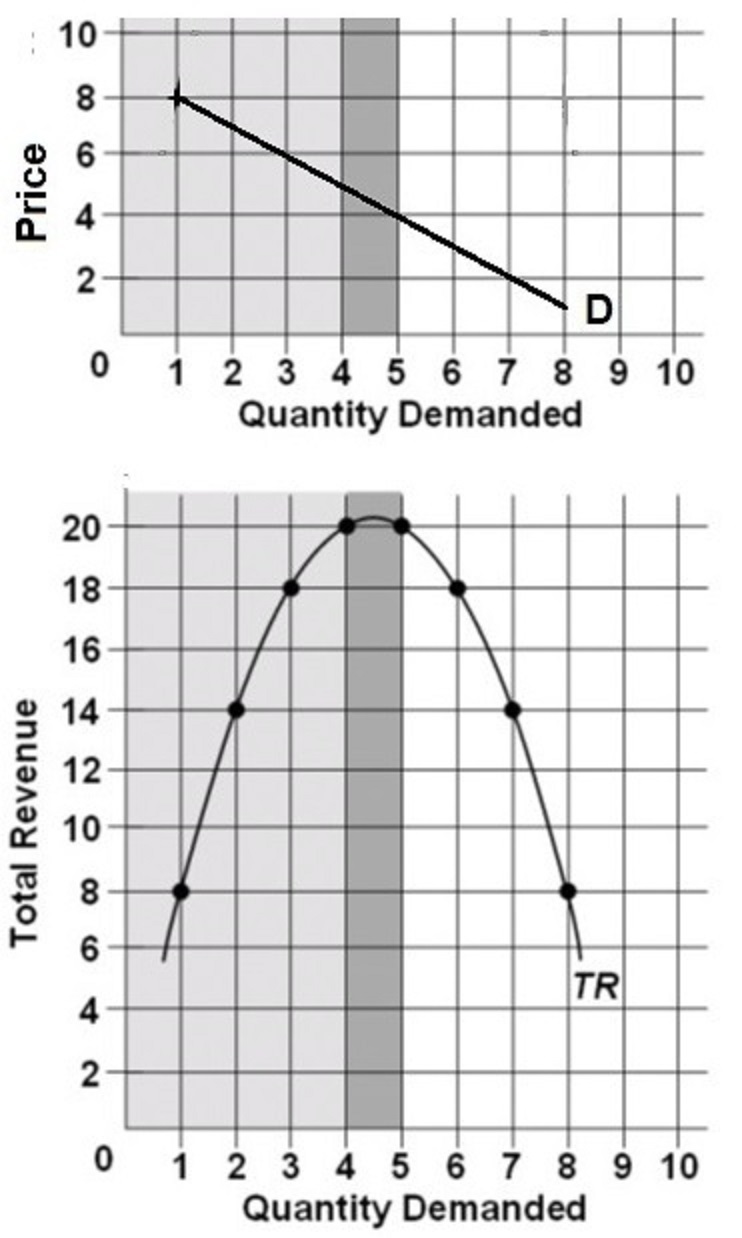
MULTIPLE CHOICE: Suppose that this
total revenue curve (see graph above) is derived from a
particular linear demand curve (see graph above). This
demand curve must be:
A. inelastic for price
declines that increase quantity demanded from 6 units to
7 units.
B. elastic for price declines that increase quantity
demanded from 6 units to 7 units.
C. inelastic for price declines that increase quantity
demanded from 4 units to 3 units.
D. elastic for price increases that reduce quantity
demanded from 8 units to 7 units.
ELASTICITY AND INCIDENCE OF EXCISE
TAXES
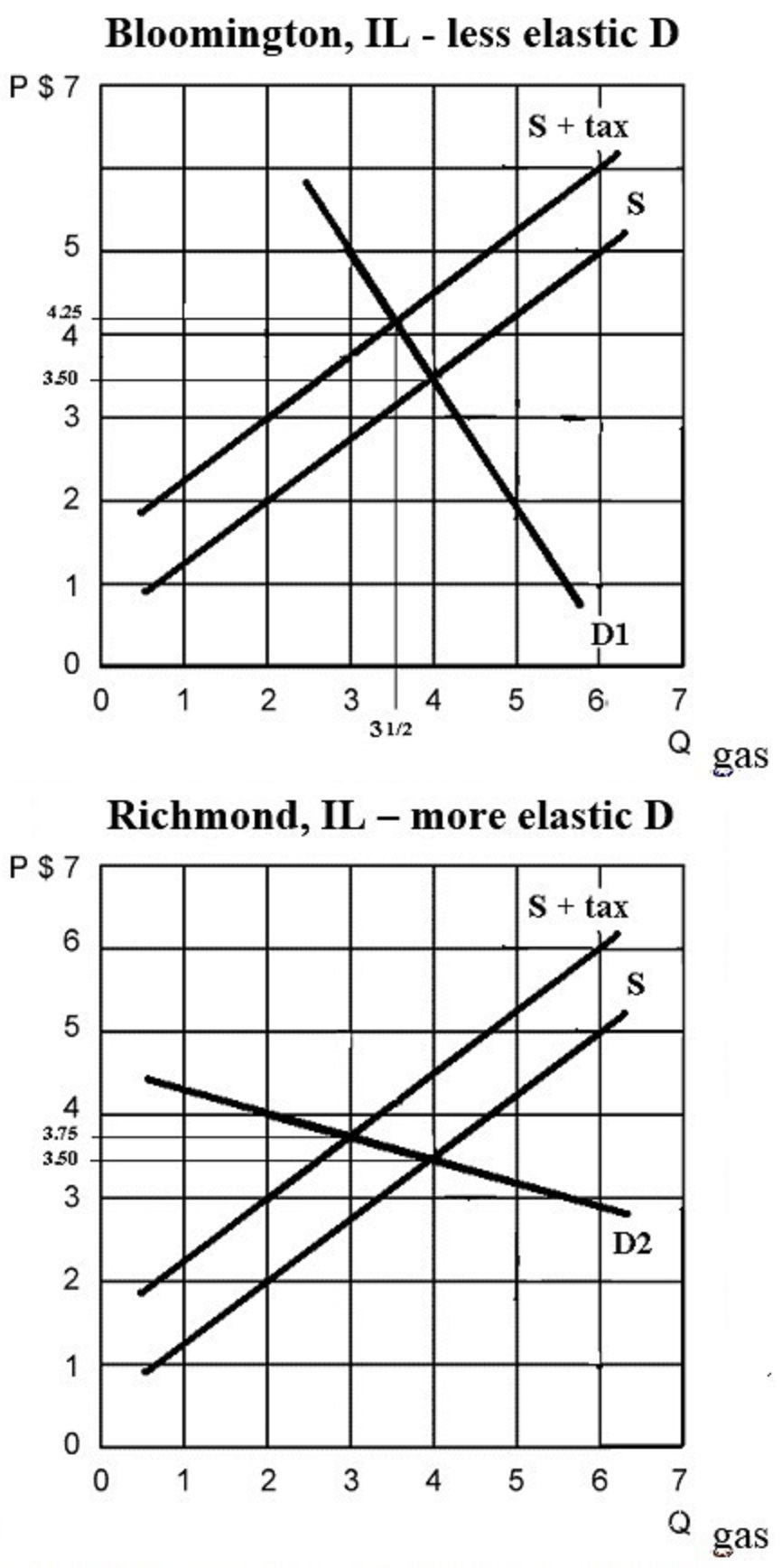
See the graphs above. Compare the
following when demand is more elastic (like in
Richmond, IL on the Wisconsin border), and less
elastic (like in Bloomington IL in the center of the
state):
(1) incidence of the
excise tax
(2) effect on allocative efficiency
(3) effect on government revenue
|