|
EXPLANATION/ CHARACTERISTICS /
RESULTS
- Inclusive (Industrial) Unions try
to include all workers of a company in the union including
skilled workers and unskilled workers, assembly line
workers, secretaries, etc.
- Then they increase wages by
threatening to go on strike (all workers will stop working
which will shut down the company).
- To keep things simple assume a
competitive product market so Dlabor = MRP = VMP
- Examples:
- Autoworkers
union
- Steelworkers union
- Result:
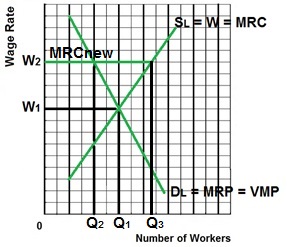
- W1 is the competitive
wage if there is no union
- W2 is the union negotiated wage
rate
- Since all workers must be paid
W2 it becomes the firms new MRC (extra cost of hiring one
more worker)
- Therefore the firm will hire Q2
workers because this is where MRP = MRCnew (the new
profit maximizing quantity to hire with the union
contract)
- Q1 is the allocatively efficient
quantity to employ (the competitive quantity) so
inclusive unions cause allocative inefficiency in the
labor market.
- At the Union wage of W2, Q3
workers want to work but only Q2 workers are hired
creating a surplus of labor.
|