|
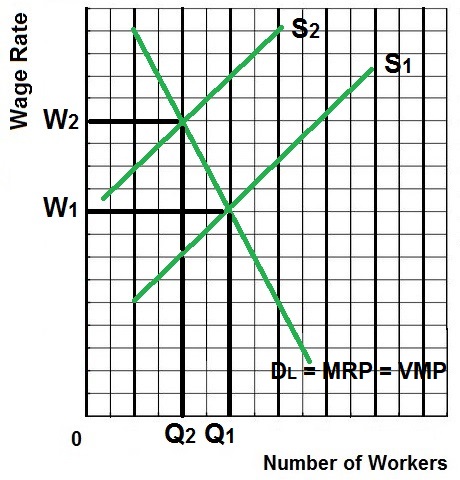
EXPLANATION/ CHARACTERISTICS /
RESULTS
- Some unions try to increase wages
by reducing the supply of labor
- To keep things simple assume a
competitive product market so Dlabor = MRP = VMP
- Examples - Some unions support:
- restricting
immigration
- laws banning child
labor
- compulsory
retirement
- shorter work week
- Craft (or Exclusive)
Unions
- A union of workers that
all possess a certain skill
- They then restrict membership in
the union through various means including high fees and
long apprenticeships
- Examples: electricians union,
carpenters union, plumbers union
- A similar technique to increase
wages is used by professional organizations like the
American Medical Association (doctors), the American Bar
Association (lawyers) and the National Education
Association (teachers) which try to set strict and
difficult requirements for getting a license to work in
their fields
- Even barbers and hair stylists
support licensing requirements that restrict how many
people can cut and style hair.
- Results:
- Therefore the firm will
hire Q2 workers at a wage of W2. This is the equilibrium
or profit maximizing quantity to hire with the union
policies.
- Allocatively efficient quantity
to hire is Q1 (where VMP = W). Exclusive unions cause
allocative inefficiency in the labor market.
|