|
EXPLANATION/ CHARACTERISTICS /
RESULTS
- A Bilateral Monopoly exists if you
have an inclusive union working for a monopsony - a single
seller of labor (the union) and a single buyer of labor (the
large company)
- Examples: Steel industry,
automobile industry, professional sports teams, aircraft
manufacturing
- To keep things simple we assume a
competitive product market so Dlabor = MRP = VMP
- Result:
- Indeterminate; we can't
tell what the quantity of labor will be or the wage rate,
it depends on negotiations between the company and the
union
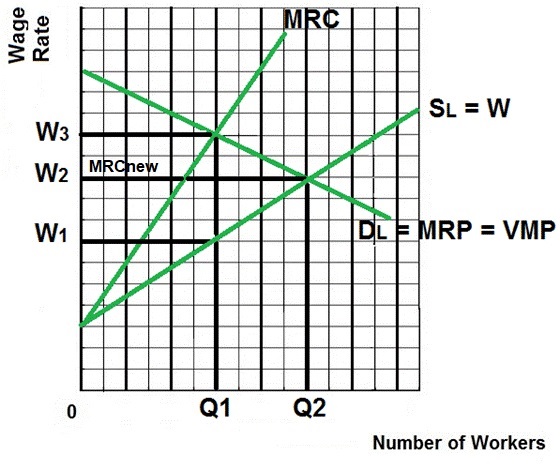
- The efficient quantity of labor
and wage is Q2 and W2 (where VMP = W)
- The company (monopsony) wants to
pay W1 and hire Q1 where MRP = MRC (alloc. Inefficiency
in the labor market)
- The union wants a wage of W3 and
the firm will hire Q1 (alloc. Inefficiency in the labor
market)
- After negotiations, the likely
resulting wage will be between W1 and W3.
- If they negotiate a wage rate of
W2 then that rate becomes the firms new MRC (the extra
cost of hiring one more worker will be the negotiated
wage rate) and the firm will hire Q2 (where MRP =
MRCnew)
- Once the union and the company
agree on a wage rate between W1 and W2:
- MORE WILL BE
EMPLOYED
- the labor market could
achieve allocative efficiency (VMP = W at
Q2)
|