|
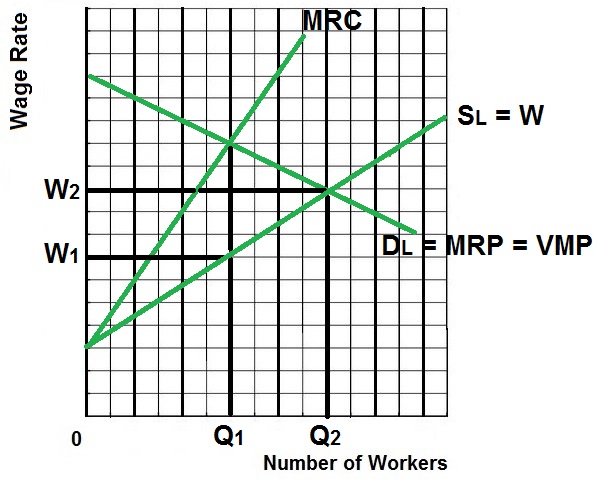
EXPLANATION/ CHARACTERISTICS /
RESULTS
- A single buyer of labor
- Examples:
- Major employer in a
small town
- A mining town in
Appalachia
- A Colorado ski town
- Firm is a "wage maker" - they will
try to pay as low a wage as possible, therefore the supply
of labor graph is upward sloping.
- MRC is higher than the wage because
when they raise wages to hire more workers they must also
raise the wages of all current employees which makes the
cost of hiring another worker very high.
- We assume a competitive product
market so Dlabor = MRP = VMP
- Results:
- Profit maximizing
(equilibrium) quantity to hire is Q1 (where MRP =
MRC)
- Wage paid is W1
- Allocatively efficient quantity
and wage is Q2 and W2 (where VMP = W)
|