|
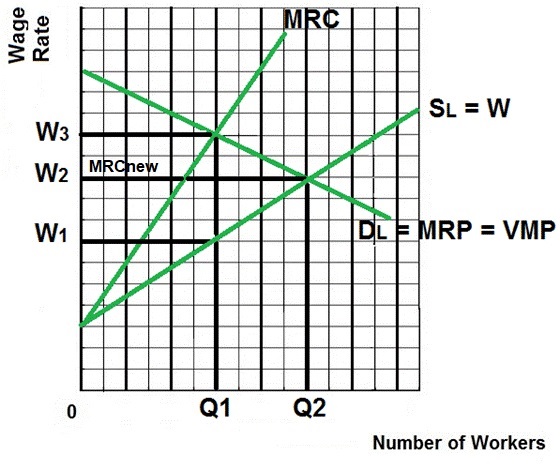
EXPLANATION/ CHARACTERISTICS /
RESULTS
- To keep things simple we assume a
competitive product market so Dlabor = MRP = VMP
- Example: Minimum wage in a
non-unionized one industry town like a steel mill town,
mining town in Appalachia, or a small Colorado ski
town.
- The allocatively efficient quantity
is Q2 (where VMP = W)
- Without minimum wage Q1 would be
employed by the monopsonist at a wage of W1 (allocative
inefficiency)
- Results with a minimum wage set at
W2:
- Wages increase from W1
to W2
- Quantity of labor hired
increases from Q1 to Q2 (where MRP = MRCnew)
- W2 becomes the
firm's new MRC curve (the extra cost of hiring one
more worker is the minimum wage that they have to
pay)
- To maximize profits firms
will hire the quantity of labor where MRP = new
MRC
- With the minimum wage the
profit maximizing quantity to hire for a monopsony
will be Q2, more than what they would hire if they
could pay a lower wage.
- The quantity of labor will be
allocatively more efficient
|