|
EXPLANATION/ CHARACTERISTICS /
RESULTS
Competitive Product Market (Pure
Competition)
- Very many
producers
- Producing a standardized
product
- No barriers to entry
- No market power
- The demand curve for the product
is horizontal (perfectly elastic) at the market
price
- Example: Agriculture
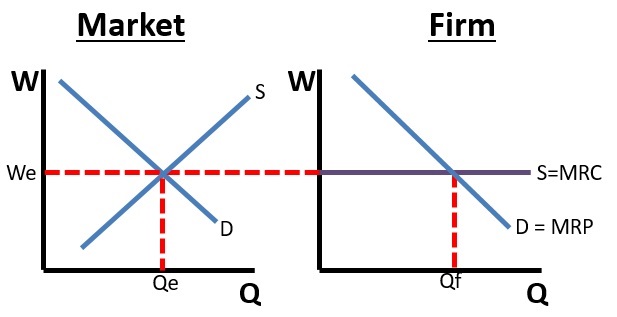
Competitive Labor Market:
- Very many qualified
workers with identical skills
- Workers are therefore "wage
takers" with no power to get a higher wage
- Therefore the supply of labor
graph (Slabor = W) is horizontal (perfectly elastic) at
the market wage
- Example: The market for
unskilled labor - Walmart hiring unskilled
workers
Example of Competitive Product Market
in a Competitive Labor Market:
- Agriculture hiring
unskilled labor
- We know that a competitive
product market is allocatively efficient in the product
market. They are also allocatively efficient in the labor
market.
- We assume a competitive product
market so Dlabor = MRP = VMP
Result:
- Profit maximizing
(equilibrium) quantity to hire is Q1 (where MRP =
MRC)
- Allocatively efficient quantity
to hire is Q1 (where VMP = W)
- A competitive labor market in a
competitive product market is efficient!
|