8b - PURE COMPETITION - LONG RUN EQUILIBRIUM AND
EFFICIENCY
From Short-run to Long-run in Perfectly Competitive Markets
(econclassroom.com 21:23)
http://www.econclassroom.com/?p=3018
Why a firm in a perfectly competitive market will only earn normal
profits (zero economic profits) in the long run.
Review:
- In a perfectly competitive market the market supply and market
demand determine the price and marginal revenue for each
individual firm in that market
- for each individual firm the demand is perfectly elastic at
the market price and the marginal revenue will be equal to the
price
- two graphs: one for the market and one for the individual firm
- supply and demand curves for the whole market which
includes all of the individual firms
- graph for the individual firm includes:
- D=P=MR
- MC
- AVC
- ATC (per unit cost of the firm's output)
- the profit maximizing quantity for the individual firm will
occur where MR = MC
- The equilibrium quantity in the market will be equal to the
profit maximizing quantity for the individual firms times the
number of firms
- The video shows a graph where a firm is breaking even and
economic profits = zero
- TR minus TC = zero
- the firm is earning a normal profit which means that its
total revenue (TR) is enough to just equal all of its explicit
costs AND the implicit costs of paying the entrepreneur (owner)
a salary to keep him/her in business
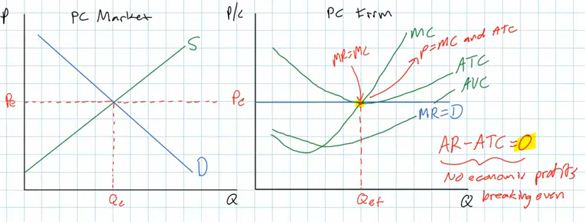
Long Run Equilibrium
A normal profit (zero economic profits) is what we would
expect individual firms in a perfectly competitive market to earn
in the long run because there are no barriers to entry.
And in long run equilibrium the P = MC (allocative efficiency,
more later) and P = minimum ATC (productive efficiency, more
later).
The individual firms are producing the quantity where their
costs per unit (the ATC) are the lowest.
if the firms produce any other quantity (less or more)
then the costs per unit (ATC) will be higher than the price and
they would earn economic losses [ME: meaning that they
could make more by quitting this business and going to their
next best alternative.]
Why do perfectly competitive firms only earn a normal profit in
the long run?
- What if they are earning short run profits due to an
increase in demand for their product?
- on the market graph the market demand will shift to the
right resulting in higher equilibrium market price
- on the graph for the individual firm the higher market
price is shown as a shift upwards of their perfectly elastic
D= P curve which is also their MR curve (D=P=MR)
- each individual firm then will respond to the higher market
price by producing a higher quantity since they will always try
to maximize their profits by producing where MR = MC, and this
now occurs at a higher level of output
- this higher price and quantity for each individual firm
will result in short run economic profits
- ME: with the higher price and quantity its total revenue
(TR) will be a lot higher
- its total costs (TC) will be only a little higher. Note
the ATC curve does not shift, but rather as firms increase
output they move slightly up their existing ATC curves
- and the yellow rectangle represents the firms new short
run profits caused by an increase in market demand
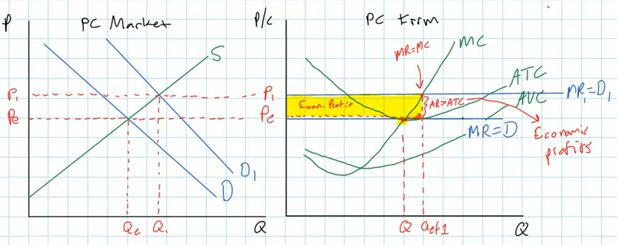
- But, what will happen in the long run?
- these short run economic profits will attract new
firms to the industry. REMEMBER: in pure competition
there are no barriers to entry so new firms can
easily enter the industry to try to capture some of these
economic profits.
- so, what will happen to our graphs if new
firms enter?
- one of the non-price determinants of supply is the
number of producers. If the number of producers goes up,
then the market supply will increase and shift to the
left.
- this will cause the market price to fall and the
P=D=MR curve for the individual firms to fall
- the individual firms then will no longer be earning
short run profits and in the long run they will be back
to zero, or normal, profits
- Entry Eliminates Profits
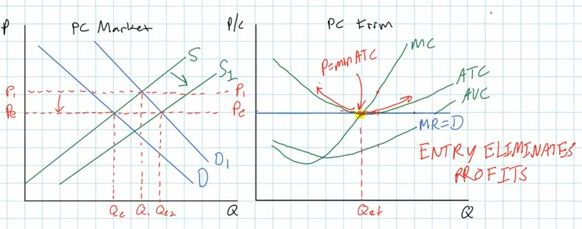
- ME: so what has happened in this perfectly competitive
industry in response to an increase in demand?
- Earlier we said: "The equilibrium quantity in the
market will be equal to the profit maximizing quantity
for the individual firms times the number of firms"
- because of the increase in demand and the increase in
supply that resulted from it the equilibrium quantity in
the market has increased from Qe to Qe2 on the graph
above.
- each individual firm is still producing the same
quantity as before (Qf) after temporarily producing a
larger quantity
- But, there are now more firms in the industry each
producing QF at the original price of Pe.
- This is good for consumers (society) . We wanted more
(increase in demand) and we got more at the same
price.
- What if they are earning short run losses due to a decrease
in demand for their product?
- Assume that initially all individual firms are earning zero
(normal) profits
- if demand decreases the market demand curve will shift to
the left and the equilibrium price will fall
- for the individual firms this means that their D-P- MR curve
will shift downward
- firms always want to maximize their profits so they will
produce the quantity where MR=MC, which is now at a lower
quantity
- and at this new profit maximizing quantity the price is now
below their ATC and they will now be earning economic losses.
- price is lower, so TR is lower
- ATC is now higher
- so their ATC is now > P
- ME: Price (P) and Average Revenue (AR) mean the same
thing
- and Profits = TR - TC = will be negative (economic
losses)

- How will firms respond to these short run economic losses?
- Exit Eliminates Losses
- due to the short run losses some firms will leave the
industry
- remember an economic loss means that they can make
more at their next best alternative
- and since there are no barriers to entry or EXIT, it
is easy for firms to leave and go to their next best
alternative
- this will decrease the number of producers and decrease
the market supply
- causing the equilibrium market price to increase
- for each individual firms this will shift their D = P =
MR curve upward
- and they will respond by producing where MR = MC which
will be at a higher quantity and they will be earning normal
(zero) profits again
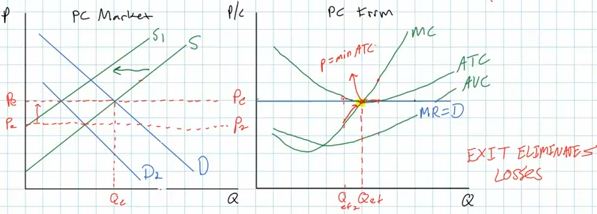
- after all adjustments the price will again be equal to
the minimum ATC, where the MC crosses the ATC
- and P = ATC = MC
- ME: So, in the long run in a perfectly competitive market
we will always get:
- normal (zero) profit
- P = minimum ATC
- P = MC
- Next lesson: Perfect Competition and Efficiency
8b - Allocative and Productive Efficiency in Perfectly
Competitive Markets (econclassroom.com 19:35)
http://www.econclassroom.com/?p=3066
Why a firm in a perfectly competitive market will achieve
allocative and productive efficiency in the long run.
Introduction
- "In order to understand what makes less competitive markets
inefficient, we first must understand what it is that makes
perfectly competitive markets efficient."
- Imperfectly competitive markets: monopoly, oligoply,
monopolistic competition
Review
- Productive efficiency:
- productive efficiency is producing at the lowest cost
- on a graph this is the lowest point on the ATC curve
(minimum ATC)
- this means the firm is using its resources wisely and not
wasting any resources
- "Productive efficiency occurs if the price of the good is
equal to the minimum ATC"
- ME: and, as we should already know, the MC curve crosses
the ATC curve at the lowest point of the ATC, so we find the
productively efficient quantity by finding the quantity where
MC = ATC
- Allocative Efficiency
- when the quantity of output produced achieves the greatest
level of total welfare (ME: satisfaction) possible
- producing the quantity where the consumer and producer
surplus is maximized
- ME: producing the quantity where MSB = MSC (marginal social
benefit = marginal social cost from chapters 3 and 5)
- ME : producing the quantity that maximizes society's
satisfaction
- ME: producning more of what prople want and less of what
they don't want (more music downloads and less CDs)
How Perfectly Competitve Marlkets achieve Productive Efficiency in
the long Run
- Productive efficiency:
- productive efficiency is producing at the lowest cost
- on a graph this is the lowest point on the ATC curve
(minimum ATC)
- this means the firm is using its resources wisely and not
wasting any resources
- "Productive efficiency occurs if the price of the good is
equal to the minimum ATC"
- ME: and, as we should already know, the MC curve crosses
the ATC curve at the lowest point of the ATC, so we find the
productively efficient quantity by finding the quantity where
MC = ATC
- firms achieve productive ifficiency if P = MC = ATC
- On the graph of a perfectly competitive firm in long run
equilibrium
- the firm will produce the4 quantity where MR = MC because
this is its profit maximizing quantity (Qf on the graph
below)
- and, we can see that the profit maximizing quantity is also
the quantity where the ATC is at a minimum (Qf on the graph
below)
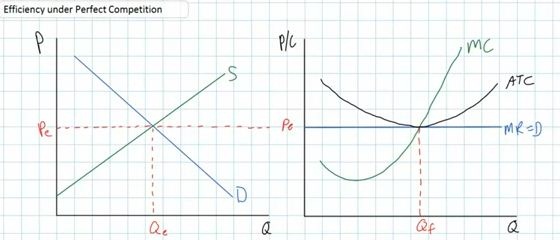
- So, purely competitive firms will achieve productive
efficiency in the long run
- what would happen if the price was higher than ATC?
- the frim would produce more
- and the profit maximizing quantity will not be at the
lowest point of the ATC curve; not where MC = ATC
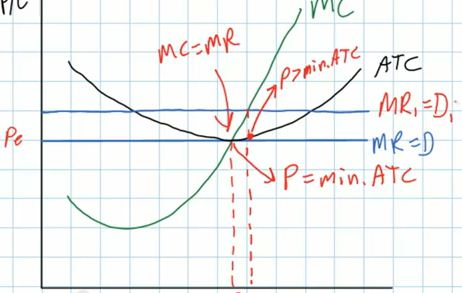
- so, in the short run this firm is not productively
efficient, but it is now earning economic profits
- and as we learned in the previous video lecture, these
profits will attract new firms, and because there are no
barriers to entry, this will increase supply and decrease
the price until each frim is again producing the quantity
where the P = minimum ATC
- and in the long run productive efficiency is achieved in
perfectly competitive markets (P = minATC)

How Perfectly Competitve Markets achieve Allocativetive Efficiency
in the long Run
- Allocative Efficiency
- definition of allocative efficiency:
- when the quantity of output produced achieves the
greatest level of total welfare (ME: satisfaction)
possible
- producing the quantity where the consumer and producer
surplus is maximized
- ME: producing the quantity where MSB = MSC (marginal
social benefit = marginal social cost from chapters 3 and
5)
- ME : producing the quantity that maximizes society's
satisfaction
- ME: producning more of what prople want and less of what
they don't want (more musinc downloads and less CDs)
- consumer surplus (CS)
- is the total well being of consumers who are willing and
able to pay a higher price than the equilibrium price in the
market
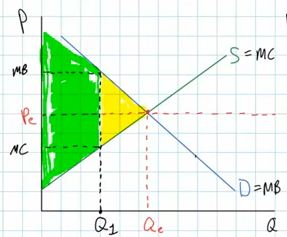
- graphically consumer surplus is the area of the triangle
below the demand curve and above the equilibrium price (the
yellow area on the graph below)
- producer surplus (PS)
- is the total welfare of producers who are able to sell
their product at a price greater than their cots of
production
- is the total welfare gained by producers who were able to
sell their product a price higher than the price they were
willing to accpt
- graphically, producer wurplus is the area above the supply
curve but below the equilibrium price (the blue traingle on the
graph below)
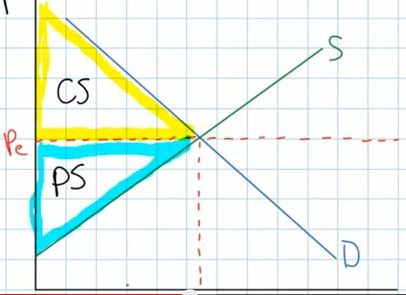
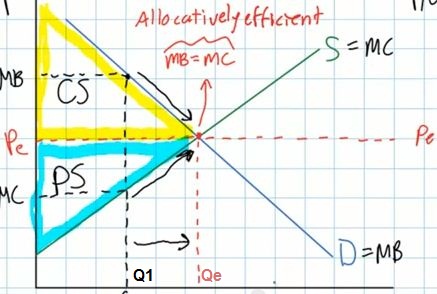
- So, in long run equilibrium a perfectly competity market will
produce the quantity where consumer and producer surplus is
maximized and MSB = MSC
- if less is produced (Q1)
- we can see that MSB > MSC and this means too little is
being produced
- ME: I have use the terms MSB (marginal social benefit) and
MSC (marginal social cost) , here the instructor is calling
these just MB and MC
- if more than the long run equilibrium quantity is produced
(Q2):
- MSB<MSC (video MC>MB) and society would be better off
with less because the extra benefits that they are getting from
one more unit of output is less than its costs
- ME: remember that all costs are opportunity costs so if
MSB<MSC this means that the costs to society of producing
more are the lost benefits that we could have gotten if we
produced something else. If MSC are high this means that
something else would give us more satidsfaction.
- and allocative efficiency is not achieved
- So allocative efficiency is achived at that quantiy where MSB
= MSC (MB = MC)
- this is alo called the "socially optimal quantity"
- For the individual firm (the graph on the right)
- MSC = MC
- MSB = P
- so allocative efficiency is achieved where P=MC
- ME: why is the price we have to pay for a product a
benefit? Isn't that a cost?
- price is a benefit to the consumer because it measure
the benefits that the consumer is getting from the
product
- if consumersm who are part of society get a lot of
benefits froma priduct they would be wiloing to pay more. If
consumers get fr=ew benefits from a pridcut they would only
buy it if the price was less
- for example I would pay more to ski in the mountains of
Colorado (where I am now as I type these notes) than I
wouyld pay to ski the hill of Wisconsin because I get more
benefits (more fun) skiing in Colorado
- ME:We know that all firms what to maximize profits so they
will produce the quantity where MR=MC. We can see on the graph
below that this perfectly competitive firm in long run
equilibrium will produce the quantity Qf to maximize its
profits. But note that this is also where P=MC.. So even though
all the firm was trying to do was to make as much money as
possible it will firm also achieve allocative efficiency. This
is the INVISIBLE HAND of competition that we talked about in
chapter 2.

- SUMMARY: Competitive frims achieve allocative efficiency in
the long run
- All firms will produce the quantity where MR=MC to maximize
theri profits
- Because of the lack of barriers to entry, competitive firms
will receive only normal profits in t he long run
- But the long run profit maximizing quantity will also be
the allocatively efficient quantity:
- the quantity where P = MC,
- the quantity where MSB = MSC
- and the quantity where the sum of the consumer and
producer surplus is maximized
- WHY?
- perfectly competitive firms achieve allocative efficiency
in the long run because the demand curve for the individual
firm is perfectly price elastic
- i.e. they are "price takers"
- Since there are very many firms producing standardized
(identical) products, firms do not have any control over the
price of the product
- this means that each individual firm can sell all they
have at the market price
- This means that the P = MR
- since they don't have to lower thier pice to sell
more
- the extra revenue that they get when they sell one more
is the same as the price
- THEREFORE: when competitive firms try to find the
quantity where MR=MC to maximize their profits, it will also
be the quantity where P=MC. So when they maximize their
profits they also achieve allocative efficiency
- P = MR for perfectly competitive firms ONLY
- we will see in other product market models that the P
> MR, i.e. the price they receive is greater than the
extra revenue (MR) they get when they sell one more
- only for price takers with perfectly elastic demand
curves does the P always equal MR
- firms in other product market models must lower their
price to sell more so, as we will see in future chapters
P>MR
- therefore, when firms in the other market models
produce the quantity to maximize their profits (quantity
where MR=MC, it will not be the allocatively efficient
quantity (where P = MC).
- To understand this better, let's see what happens if the
competitive firms produce less than the profit maximizing quantity
(Q1 on the graph below).
- at Q1 we can see that MR does not equal MC so the
frim is not maximizing its proftis
- in fact, we can see that ATC is greater than P , So TC will
be greater than TR and the firm is l
- earning a loss
- ALSO, P > MC so there is an underallocation of resources
toward this product. Too little is being produced. Remember, P
measures the MSB and Mc measures the marginal social costs
(assuminh that there are no externalities, so if P>MC then
MSB>MSC and society would be happier with more.
- Now if we assume that all firms are producing at Q1 on
their individual cost curves then the market quantity being
produced will also be less then the equilibrium. so on the
market supply and demand graph Q1 would be produced, not the
profit maximizing equilibrium quantity Qe.
- At this smaller quantity the MB to consumers is greater
than the MC
- This is allocative inefficiency because society is getting
less satisfaction
- Using the consumer and producer surplus model:
- allocative efficiency is achievced when the consumer
andproducer surplus is maximized
- this occurs at the equilibrium level of output
- but if the quantity is less than Qe, like Q1 then the
total consumer plus producer surplus is less (see the green
area on the graph below
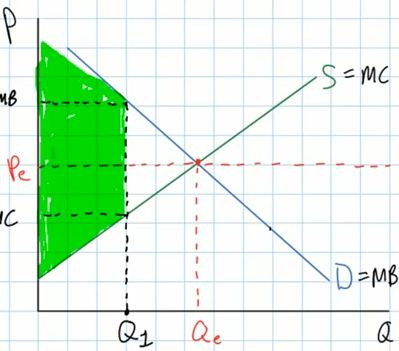
- and there is a loss of satisfaction to society (less
consumer and producer surplus) equal to the yellow triangle
on the graph below. this is what economists call the
"deadweight loss" of allocative inefficiency
- We Since less than the efficient quantity is being
produced we say that resources are underallocated to
this product, i.e. society would gain satisfaction (equal to
the yellow triangle) if more resources were used so that
more was produced. This is allocative inefficiency.
- if firms produced more than the allocatively efficient
(and profit maximizing) quantity then again we would have
allocative inefficiiency. This time MC will be > P, and
resources will be overallocated to the production of this
product. Too much is being produced. Society would be
happier if less of this was produced and more of something
else that gives us more satisfaction.
- in the market at Q2 on the graph below,
MSB<MSC
- ME: remember the opportunity cost (MSC) of consuming
this product is the satisfaction that you are not getting
from your next best alternative. So if extra benefits
that you are getting from this product (MSB or D) is less
than the benefits that you could get from something else
(MSC or S) then society would be better off with less of
this product. We say that resources are overallocated to
the porduction of this product.
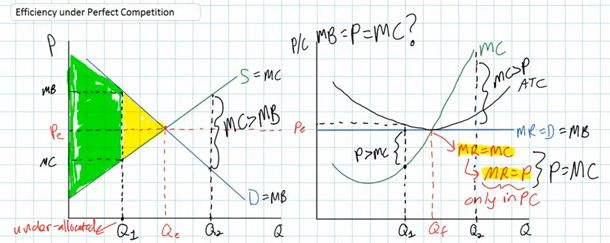
Perfectly competitive firms achieve both productive and
allocative efficiency in long run equilibrium
- they will produce the profit maximizing quantity where
MR=MC
- and this quantity will also be the productively efficient
quantity where ATC is at its minimum point
- and, this quantity will also be allocatively efficient where
P=MC










