UNIT 4
Chapter 12
12.1-1 Deriving the Factor Demand Curve
- Outline:
- A firm's demand for a resource like labor is a derived
demand. It is derived from the demand for the product that the
resource produces
- The profit maximizing rule says that a firm hires labor
up to the point at which MRP = MRC (or MRP = W in competitive
labor markets)
- to maximize profits, a firm will keep hiring workers until the
last worker adds just enough revenue to the firm to cover the cost
of that worker
- the demand for labor (by businesses) is a derived
demand, that means it resutls from the demand for the products
that the labor produces
- MRP = change in TR / change in quantity of labor
- MRP = the extra revenue that the firm gets when it hires
one more worker
- MRP = the MB to the firm of hiring another worker
- MRP = MR x MP
- MR = extra output of produding one more unit of
output
- MP = extra output from hirirng one more worker
- for purely competitive prodict market: MRP = P x MP =
VMP = value of the marginal product
- ME:
- this is just benefit-cost analysis
- they hire all workers where the MB > MC, up to where
the MB = MC
- But, how do we measure the MB of another worker and the
MC of another worker?
- MRP
- marginal revenue product
- the MB that a firm gets when it hires another worker
- Definition: the increase in the form's total revenue
derived from hiring one additional worker (or any other
variable input
- Formula: MRP = change in TR / change in quantity of
labor
- VMP
- VMP is the Value of the Marginal Output
- VMP is the value (P) of the extra output produce by adding
one more worker (MP)
- VMP = the price of the output times the extra output
produced by the last unit of labor hired
- P x MP is called the VMP
- if the firm is perfectly competitive then MRP = VMP
- MRP = MR x MP
- but in pure competition we know that MR = P
- so for firm's selling their product in a perfectly
competitve market: MRP = P x MP
- VMP = value of the marginal product = P x MP
- VMP = MRP (for firms in purely competitive product markets
only)

- What is the profit maximizing quantity of labor to hire if the
firm is purely competitive in the short run?
- ME:
- we need to know the extra benefits of hiring one more
worker and the extra costs of hiring one more worker
- then we hire up to the point that MB=MC
- MB of hiring one more worker is the MRP or the amount
that TR increase when we add one more worker
- MC of hring one more worker
- is the MRC
- margnal resource cost
- MRC = change in TC / change in quantity of labor
- so we will maximize profits if we keep hiring as long as
the worker adds more to our revenue (MRP) than it does to
our costs (MRC)
- profit maximizing rule: MRP = MRC
- Given:
- P of TVs = $100
- and the table below
- what is the profit maximizing Q of labor to
hire?
- i.e. where does MRP = MRC, or in purely competitive
product markets, where does VMP = W or MRP = W
- hire as long as the VMP is > wage you have to pay up
to where VMP = W
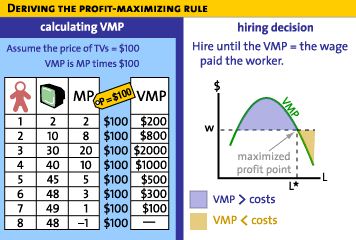
- hire L* number of workers
- thr VMP curve then is the derived demand curve ofr
labor
- it is also the MRP curve; in purely competitive product
markets VMP = MRP
- So: the demand for labor is the MRP curve
- New rule for maximizing profits in purely competitive
product markets: W = VMP or W = MRP
- New rule for maximizing profits in purely competitive product
markets: W = VMP or W = MRP
- this is really the same as MR = MC
-
Chapter 13
12.3-1 The Supply of Labor - The Determination of Wages -
Analyzing the Labor Market
- Outline:
- Demand for Labor = MRP
- Supply of Labor
- Equilibrium in the Labor Market
Economics: The Labor Market 2:37
http://www.mindbites.com/lesson/7600
Labor
Market Power and Marginal Factor Cost ($1.98 at:
http://www.mindbites.com)
A
Firm's Marginal Product Revenue Curve (Khan Academy
13:03)
How
Many People to Hire Given the MPR Curve (Khan Academy
9:02)
Minimum
Wage and Labor Markets ($1.98 at:
http://www.mindbites.com)
Economics: Analyzing the Labor Market mindbites
wage determination in imperfect labour markets 4:37 pajholden
pajholden·
ACDCLeadership
Micro Unit 5 Intro- Resource Markets 1:23
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y2Z9r4PKwI8&playnext=1&list=PL50F9C4FD0BE8FE28&feature=results_main
Micro Unit 5: Resource Market Playlist by ACDCLeadership
1. Micro Unit 5 Intro- Resource Markets by ACDCLeadership
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y2Z9r4PKwI8&playnext=1&list=PL9EB9C5438D7264E8&feature=results_main
2. 5.1 Market and Minimum Wage: Econ Concep... by
ACDCLeadership
3. 5.2 Perfectly Competitive Labor Market and Firm... by
ACDCLeadership
4. 5.3 Comparing Product and Resource Market... by
ACDCLeadership
5. 5.4 Resource Market, MRP and MRC: Econ Co... by
ACDCLeadership
5.1 Market and Minimum Wage: Econ Concepts in 60 Seconds:-
Economics Lesson
5.2 Perfectly Competitive Labor Market and Firm: Econ Concepts in
60 Seconds- 3:27 ACDCLeadership·
Perfectly Competitive Resource Market Profit Maximization 9:53
APECONREVIEWER
Minimum Wage and Price Floors 9:06 by khanacademy
http://www.khanacademy.org/video?v=j0c2vmFGbtk
EconProfessorKate
Monopsony Deadweight Loss 0:49
Monopsony Graphically 2:00

