Three Rules and Four Models
Three Rules:
|
How to find the profit
maximizing quantity:
A firm will maximize its profit (or
minimize its losses) by producing that output at which
marginal revenue and marginal cost are equal provided
product price is equal to or greater than average
variable cost.
(1) Find the quantity where:
MR=MC
(2) produce this quantity if: AR
> AVC
|
|
How to find the productively
efficient quantity:
Society will achieve productive
efficiency by producing that output at which the average
total cost (ATC) is at a minimum.
minimum ATC, or
MC = ATC
|
|
How to find the allocatively
efficient quantity:
Society will achieve allocative
efficiency by producing that output at which price and
marginal cost are equal.
P=MC
|
Four Product Market Models:
1. Competitive Market (Ch. 10)
Characteristics:
1. Number of firms:
2. Type of product:
3. Control over price:
4. Ease of entry:
5. Nonprice competition:
Examples:
Why is the D curve horizontal?
Why does P = MR?
Long-run
equilibrium graph:
Why are there only normal profits?
What happens if there are short run profits?
What happens if there are short run losses?
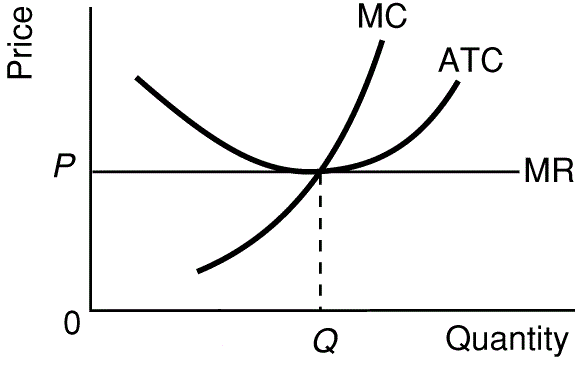
Be able to find the:
- profit maximizing quantity
- profits
- allocatively efficient quantity
- productively efficient quantity
2. Monopoly (Ch. 11)
Characteristics:
1. Number of firms:
2. Type of product:
3. Control over price:
4. Ease of entry:
What are the barriers to enrty?
5. Nonprice competition:
Examples:
Why is the demand curve downward sloping?
Why is MR < P ?
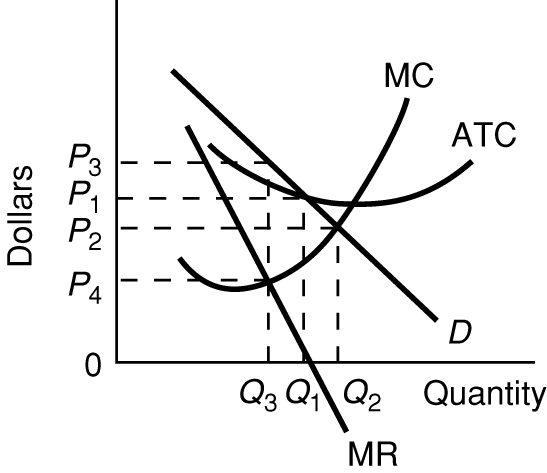
Long-Run
Equilibrium Graph
Why are there long run profits?
Be able to find the:
- profit maximizing quantity
- profits
- allocatively efficient quantity
- productively efficient quantity
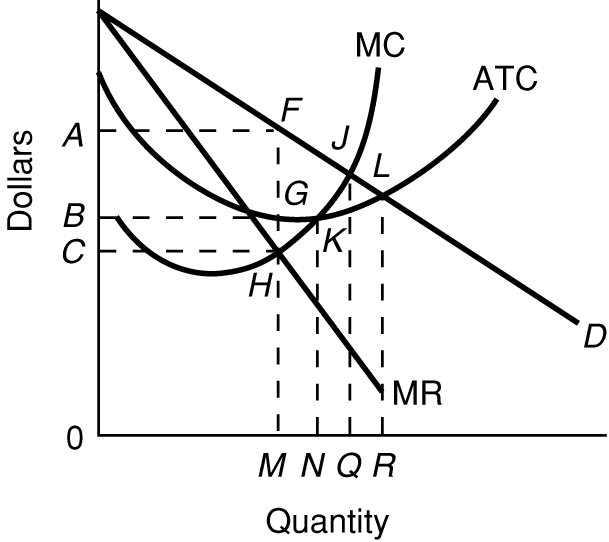
Natural Monopoly
How can you tell from this graph that this is a
natural monopoly?
What are some examples of natural monoplies?
Explain WHY it is more productively efficient for there to
be only one producer"
(WHY are there natural monopolies?)
Be able to find the:
- profit maximizing quantity
- allocatively efficient quantity
- productively efficient quantity
- "fair-return" price and quantity
3. Monopolistic Competition (Ch. 12)
Characteristics:
1. Number of firms:
2. Type of product:
3. Control over price:
4. Ease of entry:
5. Nonprice competition:
Examples:
Define:
Concentration ratio:
(Is the concentration ratio HIGH or LOW for
monoplistically competitive industries?)
Herfindahl index:
(Is the Herfindahl index HIGH or LOW for
monoplistically competitive industries?)
Long-Run
Equilibrium
Why are there only normal profits in the long
run?
What happens if there are short run profits?
What happens if there are short run losses?
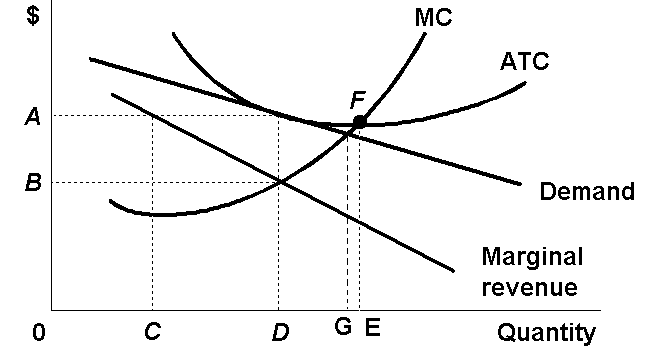
Be able to find the:
- profit maximizing quantity
- profits
- allocatively efficient quantity
- productively efficient quantity
4. Oligopoly (Ch. 12)
Characteristics
1. Number of firms:
2. Type of product:
3. Control over price:
4. Ease of entry:
5. Nonprice competition:
Examples:
Define:
Concentration ratio:
(Is the concentration ratio HIGH or LOW for
oligopolistic industries?)
Herfindahl index:
(Is the Herfindahl index HIGH or LOW for
oligopolistic industries?)
What are the three oligopoliy pricing models?
What are the assumptions behind the kinked demand
curve?
Long-Run
Equilibrium
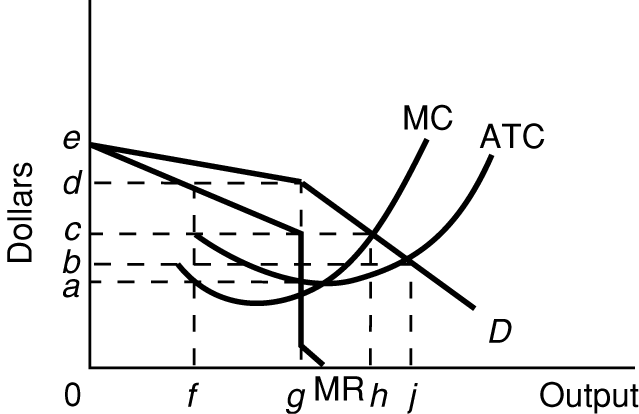
Be able to find the:
- profrit maximizing quantity
- allocatively efficient quantity
- productively efficient quantity




